Aug. 25, 2022
Joint Feasibility Study in South Korea for Producing Hydrogen by Ammonia Decomposition using Photocatalyst
Sumitomo Corporation Group has agreed to jointly start a feasibility study (hereinafter, “this study”) for producing hydrogen by ammonia decomposition using photocatalyst (※) in South Korea with US hydrogen technology startup Syzygy Plasmonics Inc. (hereinafter, “Syzygy”), Lotte Chemical HQ (Lotte Chemical Corporation and Lotte Fine Chemical Co., Ltd.) of the Lotte Group in South Korea.
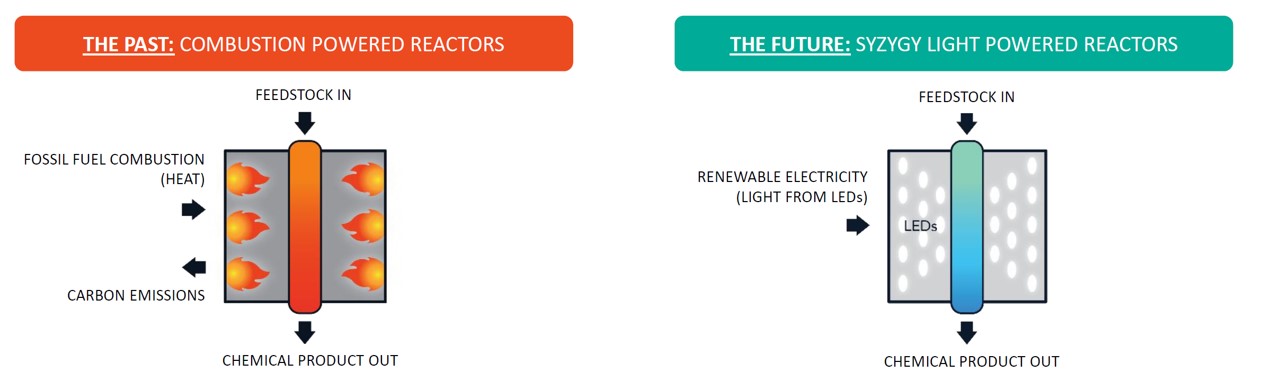
Syzygy, a startup company founded in 2017, has the world’s most advanced technology for electrifying various chemical reactions, including that for hydrogen production, using a photocatalyst developed by Rice University in the US. This technology enables the production of hydrogen with lower energy, lower cost and higher efficiency than ordinary pyrolysis. Sumitomo Corporation Group has been working on the development of hydrogen/ammonia related business utilizing Syzygy’s technology together with knowledge accumulated on the latest hydrogen/ammonia technology since its investment in the company in 2019.
In South Korea, revised draft of the hydrogen law, including substantial obligations to utilize clean hydrogen and ammonia for the power generation business, passed the National Diet in May. Thereafter, various efforts have increasingly been taken to achieve co-/mono-firing of hydrogen and ammonia, which is expected to result in large-scale demands with regard to hydrogen/ammonia in the future. In this study, Lotte Chemical HQ, the largest ammonia distribution company in South Korea, and Sumitomo Corporation Group, which is aiming to build a global ammonia supply chain, will verify the world’s first hydrogen production by ammonia decomposition using Syzygy’s electrochemical technology using photocatalytic reactors.
Considering hydrogen as one of the important energies for the future of a decarbonized society, Sumitomo Corporation Group has multilaterally worked on the development of hydrogen-related businesses, such as a “locally produced for locally consumed” type hydrogen business that makes the most of the characteristics of hydrogen and the relevant region; large-scale hydrogen value chain business to promote mass production, transport/storage, and use of hydrogen; and investment in new technologies. For ammonia as well, Sumitomo Corporation Group is examining/promoting various kinds of businesses, such as the development of a competitive supply network for clean ammonia, the design and development of ammonia bunker vessels, and construction of a supply chain including marine transport, storage, and other related infrastructure development. In order to achieve the long-term target of “carbon neutrality by 2050” to mitigate climate change and greatly contribute to “achieving a sustainable energy cycle,” the Group is increasingly making various kinds of efforts to promote the hydrogen/ammonia related business.
- Photocatalyst
A substance that accelerates various chemical reactions and increases the energy of chemical substances via radiated light. Syzygy’s photocatalyst enables the induction of various types of chemical reactions at relatively normal temperatures, which were conventionally induced at a high temperature and under high pressure. The technology can provide the advantages of reduced CO2 discharge from chemical reactions, high efficiency, and lower cost. It is expected that the photocatalyst will enable the wider spread of hydrogen, since various chemical reactions including electrolysis of water, reformation of vapor and natural gas, and decomposition of ammonia, are required in the hydrogen production process.