- TOP
- Enriching+TOP
- Contributing to big LNG project
2023.10.1
Business
Contributing to big LNG project
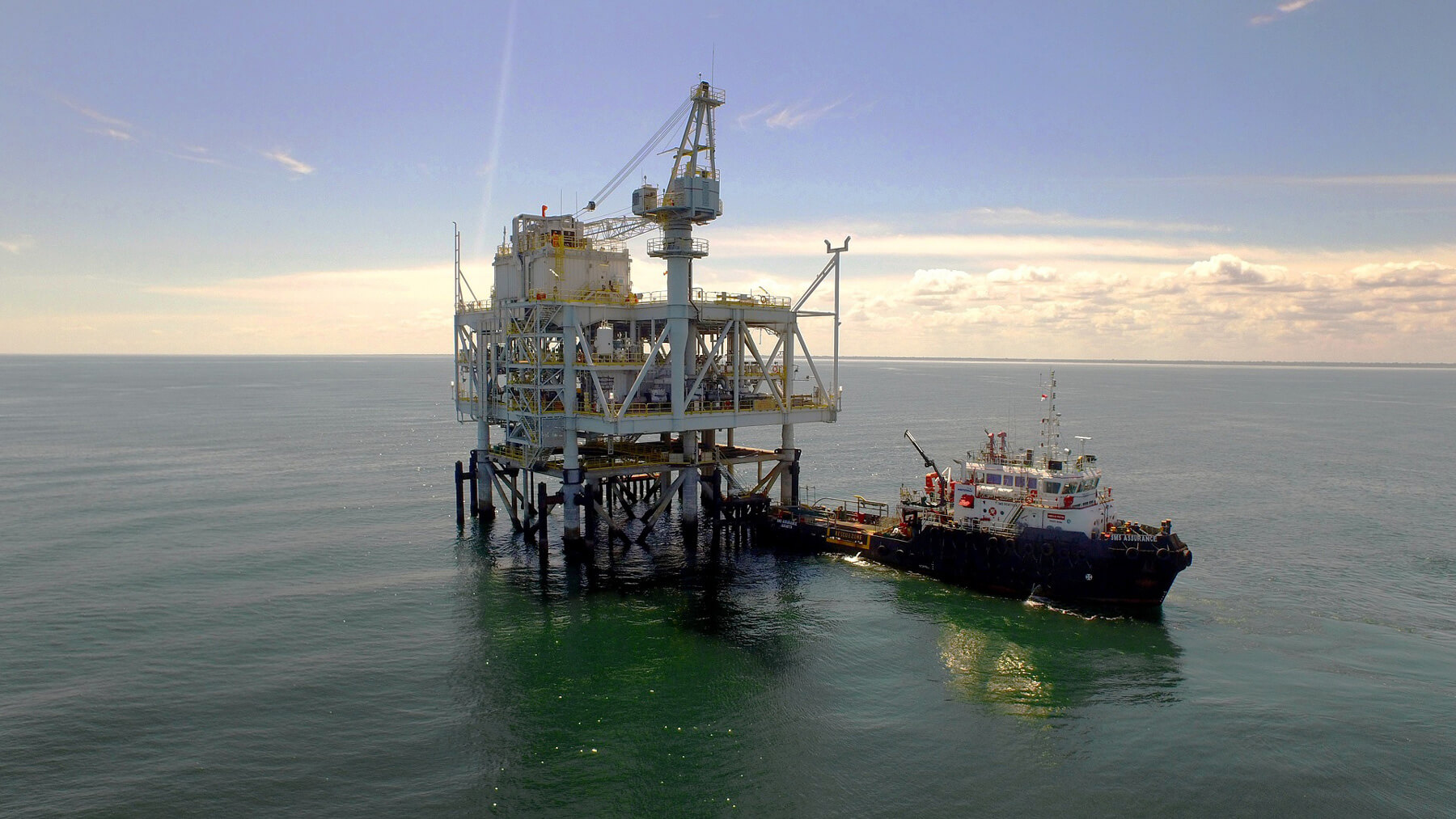

Natural gas generates lower levels of CO2 emissions from burning compared with other fossil fuels. The Sumitomo Corporation Group has participated in the liquified natural gas (LNG) development project launched in Indonesia in the 1990s through its member company, LNG Japan Corporation. The project has started operations to produce gas to support many industries and people’s lives in a number of countries in Asia. The following story describes our endeavors to pursue the “mitigation of climate challenge” and “Development of local society and economy” at the same time.
This content was originally published in October 2020.

Project name: “Strong”
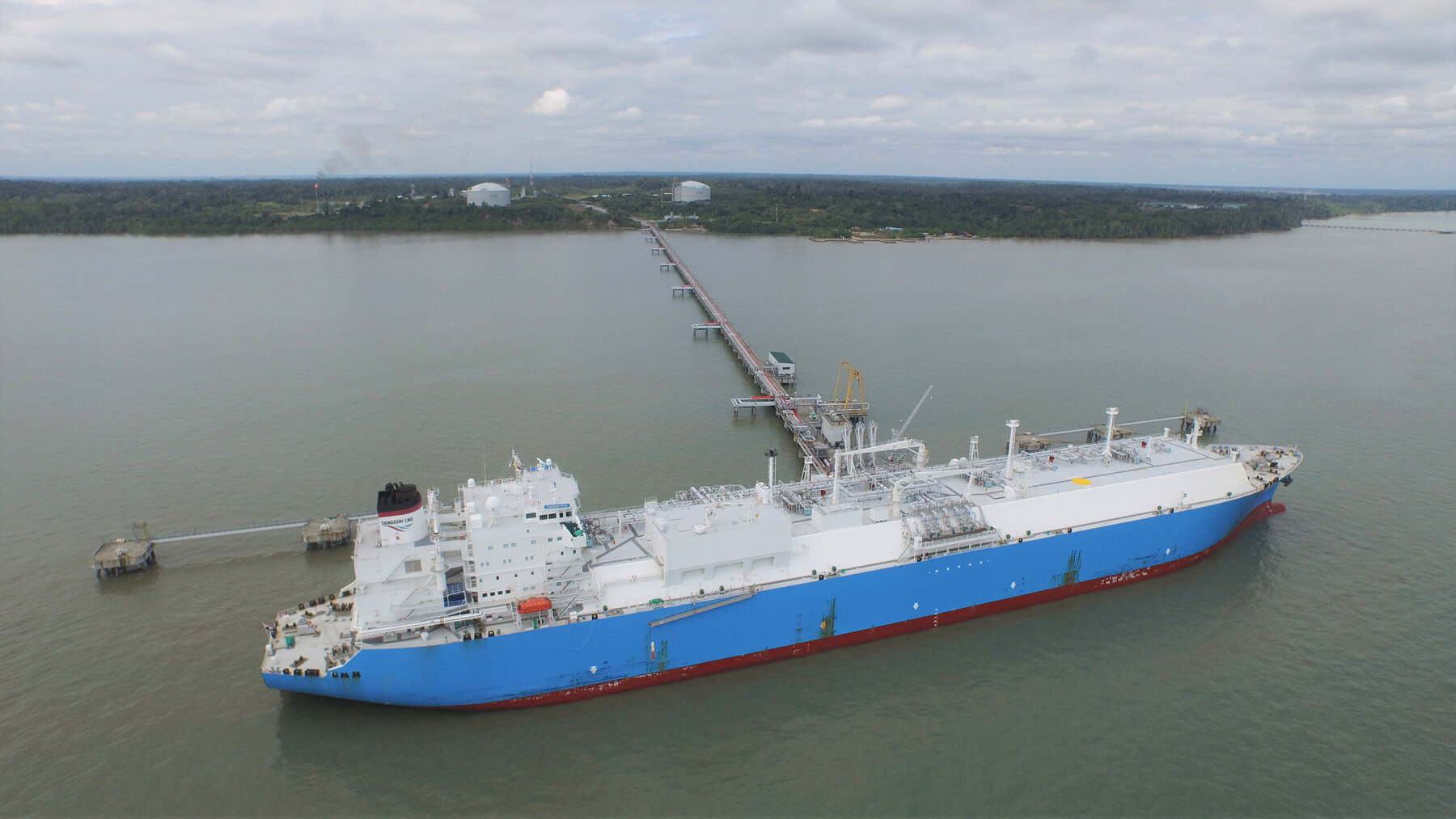
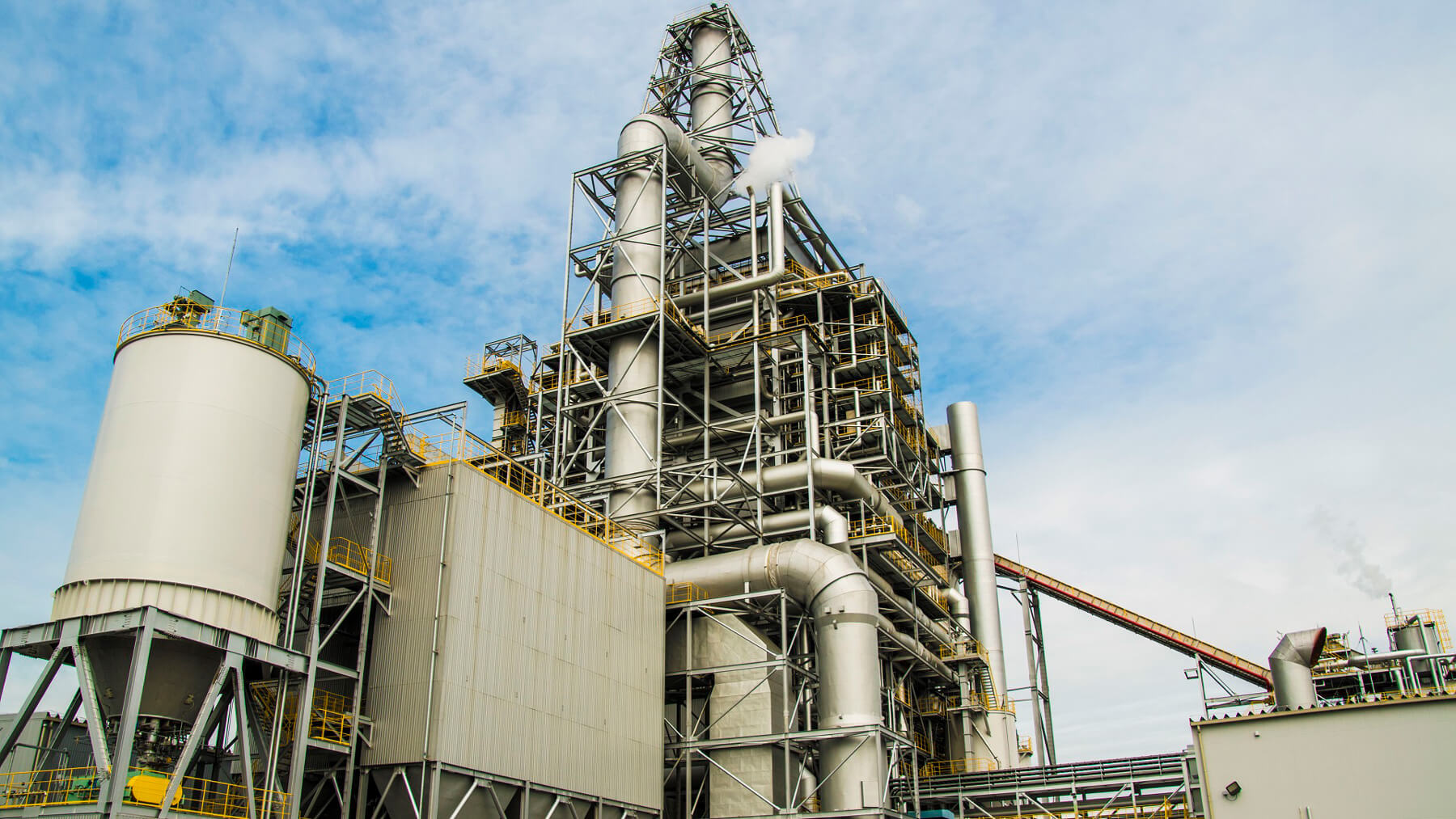
Natural gas, which emits relatively low levels of CO2 during combustion compared with other fossil fuels and is therefore low in environmental impact, is widely used as a fuel, for example, for thermal power plants. There are two main methods for transporting large quantities of natural gas, through pipelines connecting gas production and consumption sites, and by tankers. For countries like Japan, which is surrounded by the sea and cannot be supplied through pipelines, or in cases where long-distance transport makes pipelines uneconomical, shipment by tanker is essential. For the sake of convenient transportation by tankers, natural gas, which is in a gaseous state at room temperature, is reduced to a liquid state, namely liquefied natural gas (LNG), and 1/600th its original volume by cooling it to minus 162C°.
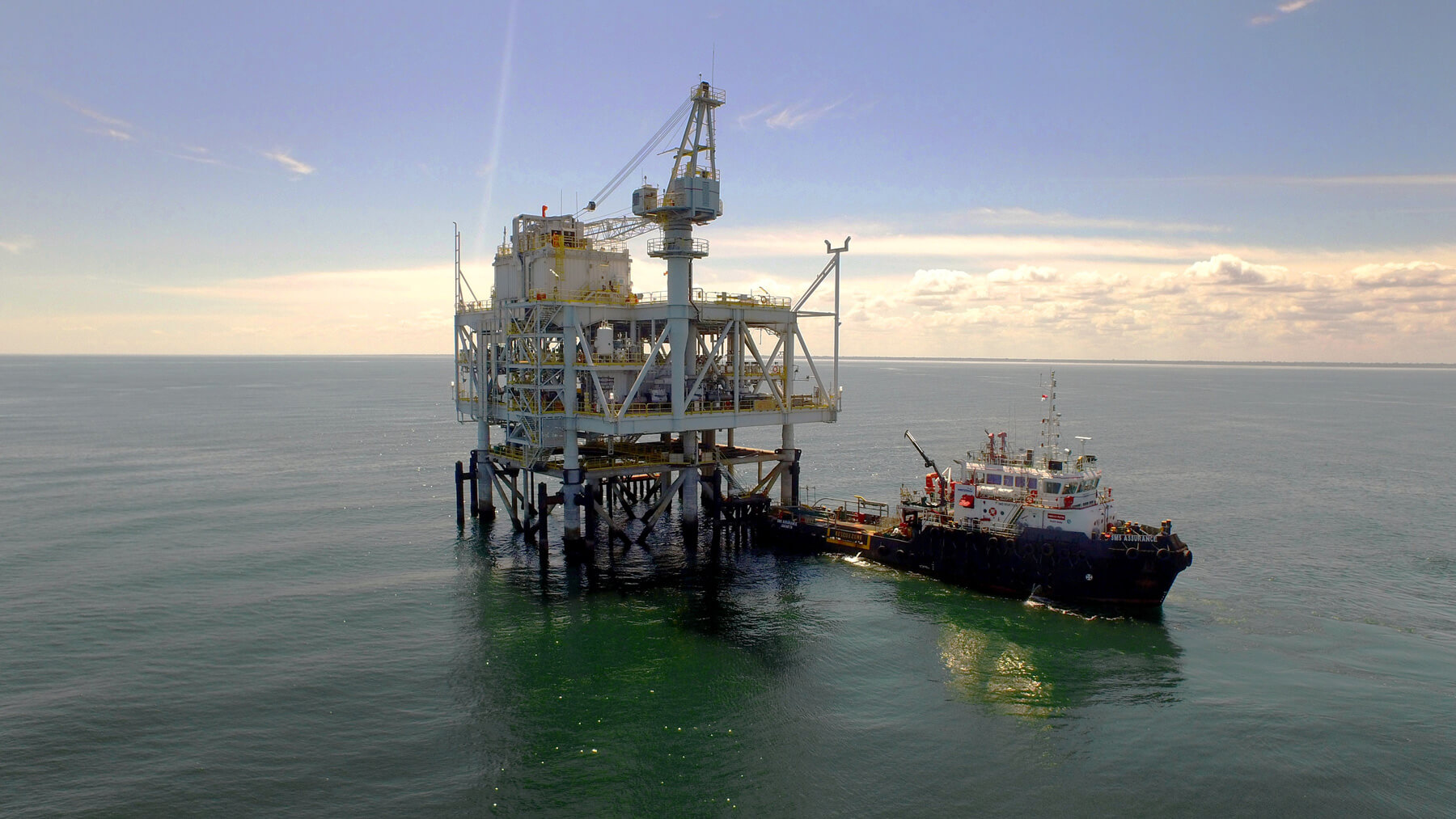

Momentum to develop the LNG businesses picked up in the 1990s on the back of Indonesia’s major large-scale natural gas field in Papua Barat Province. A project named by President Suharto "Tangguh (meaning "strong" in Indonesian)", was discovered in 1994 to extract natural gas from this field and to ship it as LNG. A number of Japanese companies participated in the Tangguh Project, providing financial and other support. LNG JAPAN CORPORATION, an affiliate of Sumitomo Corporation, was one of the project partners.
LNG sustains electricity supply after the Great East Japan Earthquake
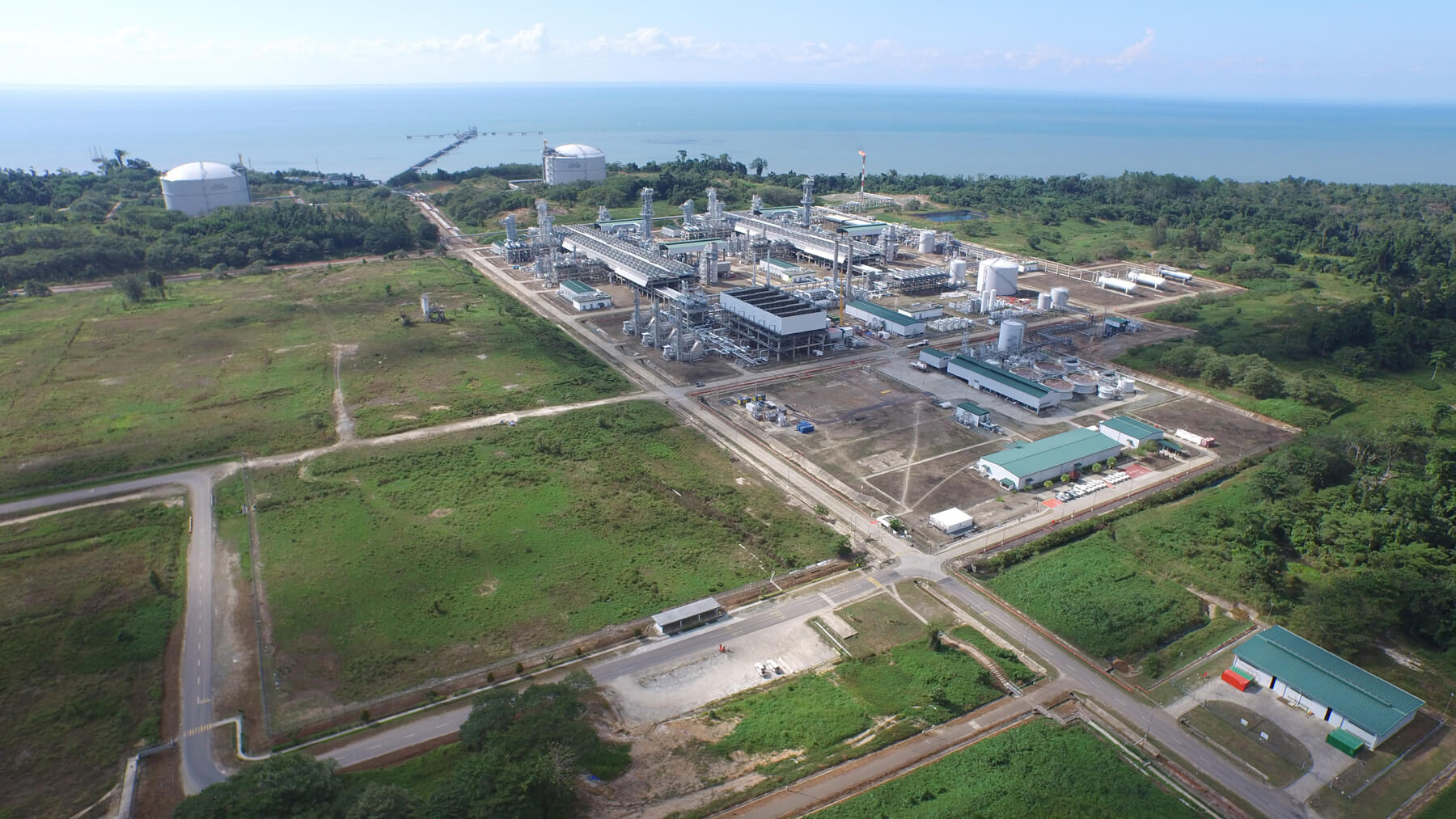

After the Great East Japan Earthquake on March 11, 2011, the presence of thermal power generation increased, owing to the decrease in power supply sourced by nuclear power plants in Japan. In response, shipment destinations of LNG produced under the Tangguh Project were partially rerouted to Japan to support stable power supply in the country. This LNG Supply helped to carry the modern life of Japanese people even after the earthquake.
In 2016, a final investment decision was made to expand the Tangguh LNG Project, and by 2023 the LNG third trainwas added, increasing LNG production capacity from 7.6 million tons per annum (mtpa) to 11.4 mtpa. With 75% of the additional LNG volume being supplied to Indonesia's state electricity company, the expansion project satisfies the country's growing energy demand. The remaining 25% is sold to The Kansai Electric Power Company, thus contributing to Japan's national energy security. Furthermore, in 2024, a new investment decision was made to pursue another expansion project, which includes Indonesia’s first large-scale CCUS(Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage) initiative. This is expected to play an important role in advancing CCUS technologies in the country.
Long-term commitment
LNG projects require a long time to develop. Only few companies are capable of making continuous contributions for over decades of business operations and in finance. Companies are put perseverance to the test during the course of promoting LNG projects.
Sumitomo Corporation will continue to tenaciously pursue LNG project development and operation with the aim of providing stable supplies of natural gas to countries with scarce natural resources, such as Japan and South Korea, and supporting development of the industry and people's livelihood in China and Southeast Asian countries through energy.