- TOP
- Enriching+TOP
- What will be the future brought with the next generation of communication, 5G and local 5G
2023.10.1
Business
What will be the future brought with the next generation of communication, 5G and local 5G

With the spread of IoT, everything is connected to the Internet and communication needs are diversifying. Under these circumstances, the fifth-generation mobile communication system (5G) is attracting a lot of attention. But have you ever heard of local 5G, which will be institutionalized in 2020 alongside 5G? Local 5G refers to a mechanism in which municipalities and businesses can build and operate their own 5G communication networks in limited areas according to diversifying local or industrial needs.
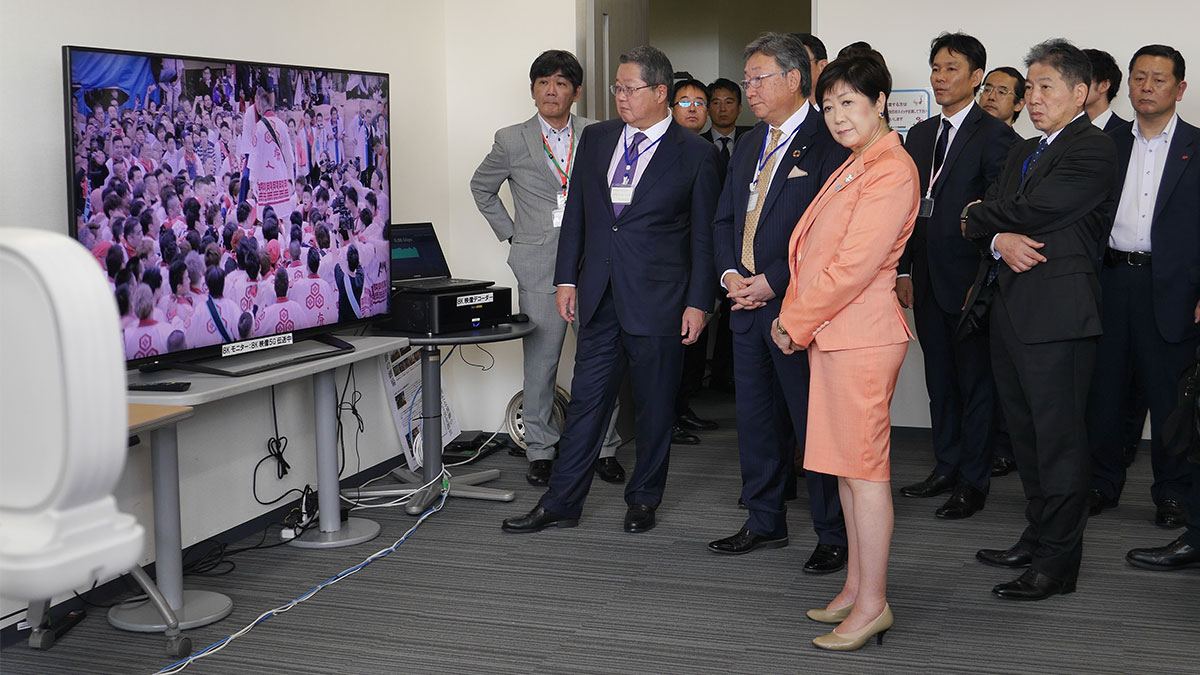
Having obtained an experimental radio station license for 5G from the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC) in late June 2019, Sumitomo Corporation carried out Japan’s first indoor/outdoor pilot experiment using local 5G. In July, Sumitomo Corporation held a media tour at J:COM Tokyo, which was one of the experiment sites, to demonstrate 4K/8K video transmission using local 5G and measure the impact of changes in communication distance. More than 500 people including Tokyo Governor Yuriko Koike participated in a total of five public demonstration sessions, indicating a high level of interest among related sectors. In this article, I would like to outline local 5G and introduce Sumitomo Corporation’s initiatives.
This content was originally published in November 2019.
-

Mass Media Relations Team, Corporate Communications Department
Haruka Nukaya
Since joining Sumitomo Corporation in 2018, I have been in charge of media relations for the Media & Digital Business Unit as well as HR dept. and media surveys. My ideal day off is enjoying the Takarazuka Revue and other theater performances or playing with my dog and cat at my family home in Nagoya, which is actually difficult due to the distance from Tokyo. I’m praying for a future when I can visit a different town just by opening a door.

- 5G/local 5G: next generation of communication with various possibilities
- Acquiring knowledge of local 5G through cooperation with cable TV industry
- Japan’s first local 5G pilot experiment using millimeter band
- What does a world with 5G/local 5G look like?
- (Bonus) Demonstration of 5G base station sharing
5G/local 5G: next generation of communication with various possibilities
Wireless communication has undergone a generation change in global standards every 10 years. 5G, namely the 5th generation, is characterized by high speed, large capacity, low latency and the massive interconnection of devices, and is likely to offer possibilities for fundamental change in various industries.
For example, when high-speed large-capacity communication is achieved with 5G, larger video data can be distributed. It may become possible to receive video of a sport from small cameras set up in a stadium with your smartphone and watch the game from your preferred angle. That can only be possible with 5G because of the heavy load on the network. Additionally, low-latency communication will enable transmission of video and voice data on a real-time basis, allowing telesurgery using high-definition video as well as remote operation of construction systems and robots. Smart agriculture, i.e., agriculture using ICT, and automated driving will also become possible with 5G.
While major mobile carriers will provide 5G networks, local 5G will also be commercialized. Local 5G allows small organizations to build their own 5G communication networks according to their needs. You can use 5G for your own wireless communication if you obtain a license from MIC on the proviso that your use is limited to within a certain area.
Compared with 4G, 5G communication uses a higher frequency band, so that the signal covers smaller areas. Therefore, more base stations must be built to spread 5G nationwide, which takes time. However, the use of local 5G enables areas that lag behind in coverage by major carriers, as well as mountainous areas or other locations where signals cannot reach, to benefit from 5G at an early stage. Furthermore, locally built networks are less likely to be affected by server congestion or other communication failures as well as disasters in other areas. Local 5G is therefore suitable for an environment where many terminals connect to a network within a limited area, such as stadiums, concert venues, schools and businesses.
I can imagine the institutionalization of local 5G resulting in new services that are based on unique ideas or address area-specific needs, and understand why 5G is drawing so much attention.
Acquiring knowledge of local 5G through cooperation with cable TV industry

Sumitomo Corporation has worked on pilot experiments for local 5G as its strengths matched the aspirations of the cable TV industry.
The cable TV industry has a strong desire to use local 5G, as soon as it is institutionalized, for the revitalization of local communities. Cable TV infrastructure can be used as lines required for 5G networks. The affinity is very high. On the other hand, it is unknown what kind of environment allows the use of high-frequency signals for local 5G. Pilot experiments for commercialization require a coordinator that can unite many related business operators. So, Sumitomo Corporation, with know-how in the cable TV business, was singled out.
Sumitomo Corporation has been engaged in the cable TV business since 1984, and has Japan’s largest cable TV company, Jupiter Telecommunications (Renamed to JCOM in July 2021), under its group. Taking advantage of the integrated corporate strength of its group, Sumitomo Corporation will verify the seemingly infinite possibilities of local 5G through cooperation with MIC, the cable TV industry and its group companies.
Japan’s first local 5G pilot experiment using millimeter band
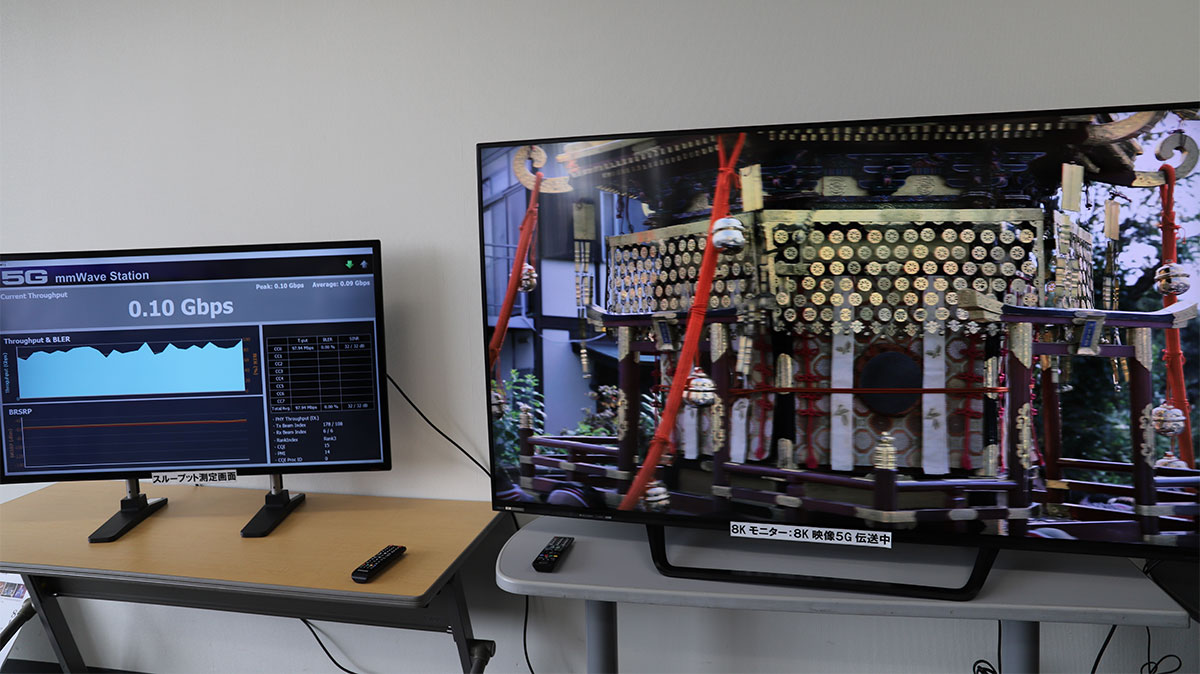
From June to August 2019, Sumitomo Corporation as an organizer of the overall experiments coordinated 16 companies and verified properties of the millimeter-wave band, the frequency band to be allocated for local 5G, and experimented with the use of cable TV infrastructure as local 5G lines.
Millimeter waves are blocked by obstacles and can be reflected easily. For property verification, impacts of such characteristics on quality of broadcasting and communication services were measured. The verification covered about 300 items that may affect the quality, including penetration of window glass, rainfall and snowfall, and changes in communication distance. To take an example of window glass, the transmittance rate depends on the type of glass, incidence angle, condensation of moisture and so on.
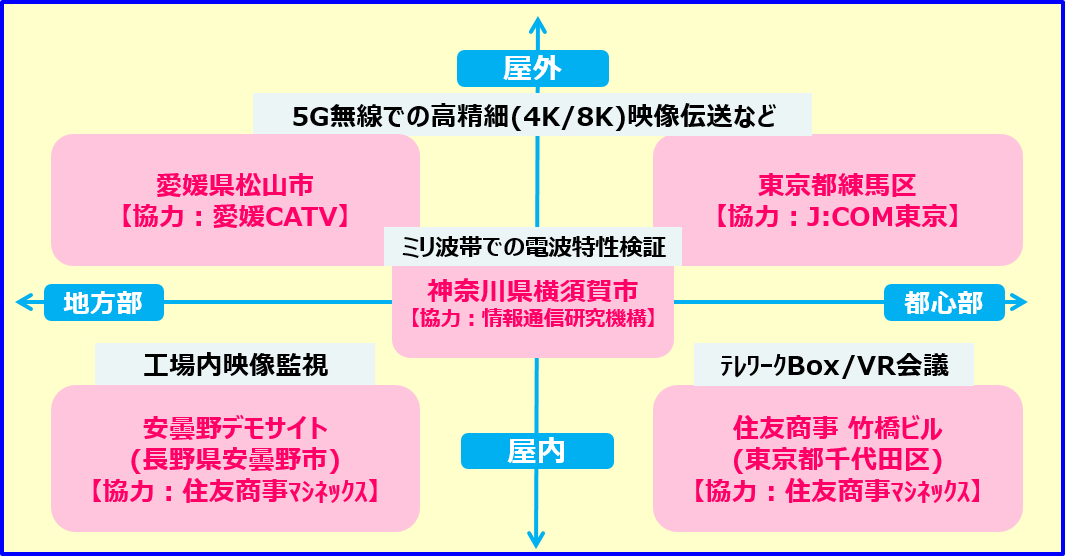
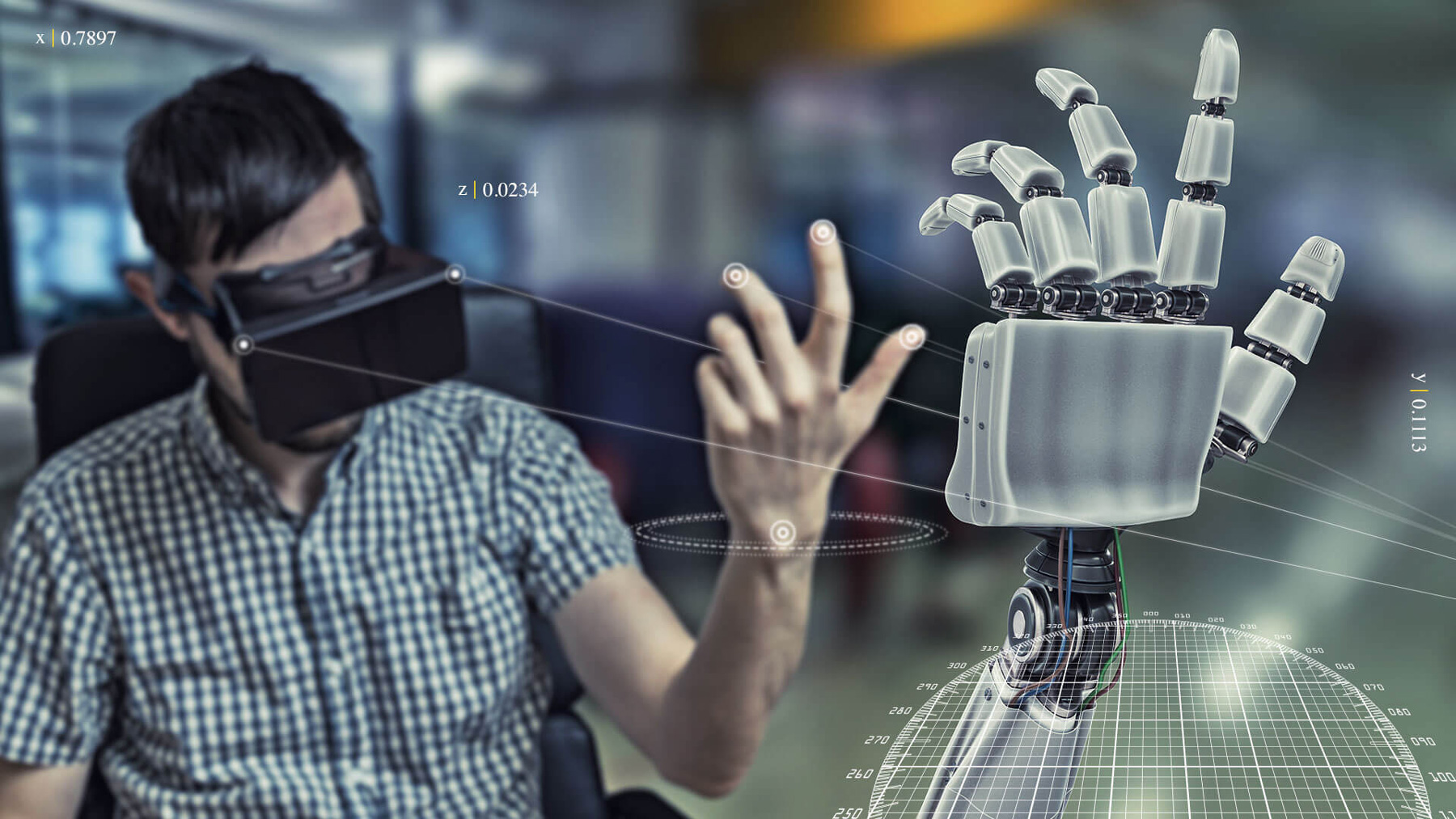
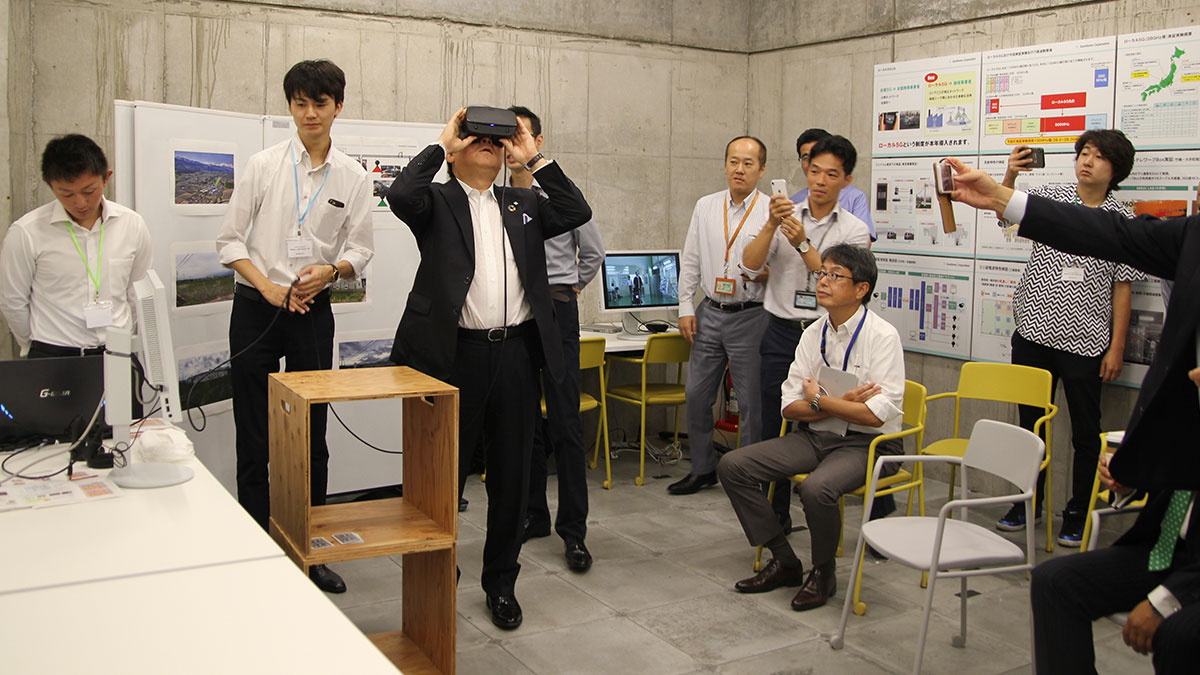
Sumitomo Corporation also conducted VR(*) conferencing using local 5G for teleworkers, remote video monitoring connecting S a plant in Kitaazumi-gun in Nagano Prefecture with the Head Office in Tokyo’s Otemachi, and a media tour.
I experienced the VR conferencing connecting the Sumitomo Corporation Takebashi Building with the Head Office in Otemachi. Wearing VR goggles at the Takebashi Building, I had a 360-degree 3D view of the Head Office meeting room. As I moved my head, I saw vivid 3D images transitioning seamlessly from one to the next, and heard the voices of people speaking without any lag. I thus got a real sense of how VR conferencing will be conducted.
I also experienced a demonstration of the monitoring of a plant in Kitaazumi-gun, Nagano Prefecture, from the Otemachi Head Office using TV screens and VR goggles. Local 5G enabled the transmission of large amounts of data from 4K 360-degree cameras set up in the plant to a radio base station on the plant premises. The VR goggles provided the wearer in the Head Office with a 360-degree viewpoint for monitoring. Unmanned monitoring that combines AI, including automated detection of machine failure and contamination, seems highly likely in the future.
*VR:
VR stands for virtual reality. VR technologies allow you to experience a virtual world created by computers as if it were the real world.




What does a world with 5G/local 5G look like?
In terms of the mobile phone, 2G allowed for emailing, 3G enabled Internet use and 4G allowed video. Advances in wireless communication have brought about dramatic evolutions in the mobile communication environment. So what will happen with 5G? At this point, no one really knows. When 4G was fully launched, services that exceeded our expectations became available. All the experts say that 5G has the potential to bring about unimaginable services that surpass 4G services.
Commercialization of 5G begins in 2020. Local 5G is institutionalized in December 2019 and its use will start soon. The more l learned about it, the more excited I became and the greater my expectations for this unseen world grew.

(Bonus) Demonstration of 5G base station sharing
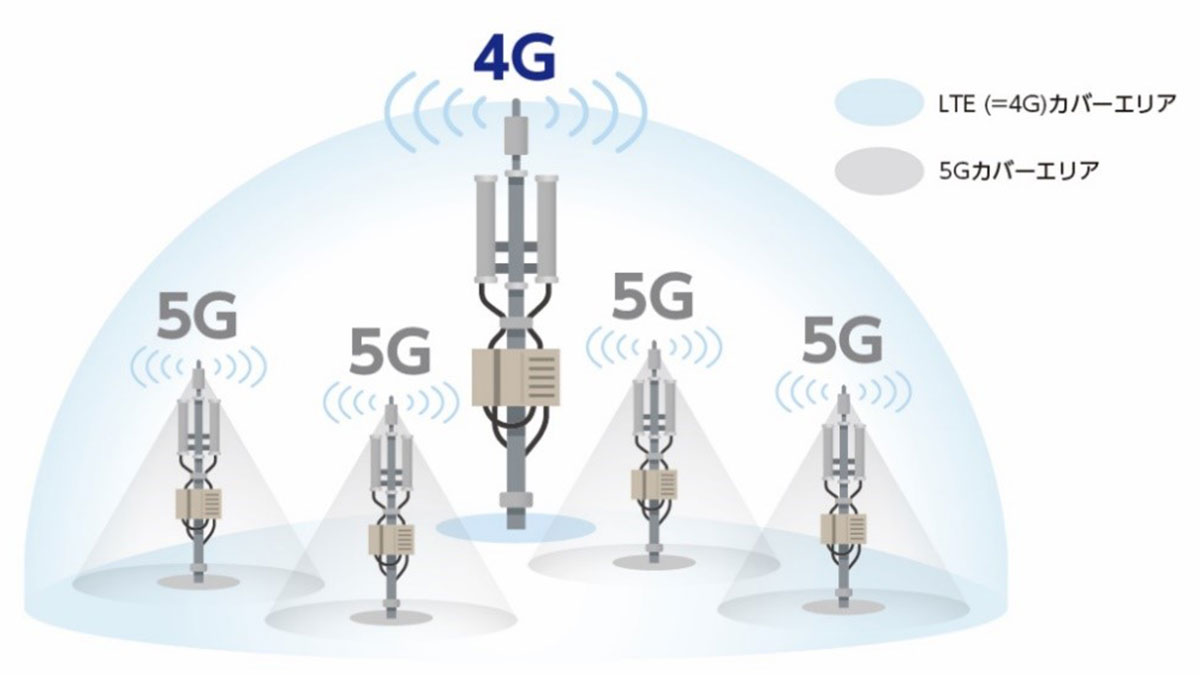
Together with Tokyu Corporation, Sumitomo Corporation will also carry out pilot experiments for sharing 5G base stations among communications companies. By January 2020, experiments will be conducted around Shibuya Station and other locations. It is estimated that, as 5G signals have a short range, five or 10 times as many base stations as needed for existing 4G will be required. This apparently creates a need for base station sharing, which also may contribute to cost reduction for communication providers.
Sumitomo Corporation has accumulated know-how in mobile communications outside Japan, including the communication carrier business in Myanmar. The Company also has knowledge in many related business areas, including communication equipment supply chain management and communication infrastructure ownership in the cable TV business. By using this expertise, Sumitomo Corporation will verify technologies for 5G base station sharing to create a foothold for commercialization.






















