- TOP
- Enriching+TOP
- Contributing to the sustainable development of local communities and the global environmental protection through the renewable energy business in Japan.
2023.10.1
Business
Contributing to the sustainable development of local communities and the global environmental protection through the renewable energy business in Japan.

This content was originally published in October 2022.

- Operating six solar and two wind power plants in Japan
- Transforming Fukushima into a leading region for renewable energy through the Abukuma Wind Power Project
- Solar power plants in Minamisoma stand as a symbol of restoration from the earthquake disaster
- Realizing optimal electricity management through Group-wide collaboration
- Developing new renewable energy power generation projects
Operating six solar and two wind power plants in Japan
Among power stations sourced by renewables such as solar, wind, biomass and geothermal energies, solar (photovoltaic) power plants generate the greatest amount of electricity in Japan. So called "mega-solar (far-over-MW photovoltaic)" power plants started to be constructed across the country in 2012, after the introduction of the Feed-in Tariff system.
In the 1990s, Sumitomo Corporation began importing polysilicon and other materials for Japanese photovoltaic panel manufacturers, while exporting their products to overseas markets. We subsequently started the development of mega-solar power plants in Europe and the United States, and from 2012, in Japan. Today, we own and operate mega-solar projects at six locations nationwide.
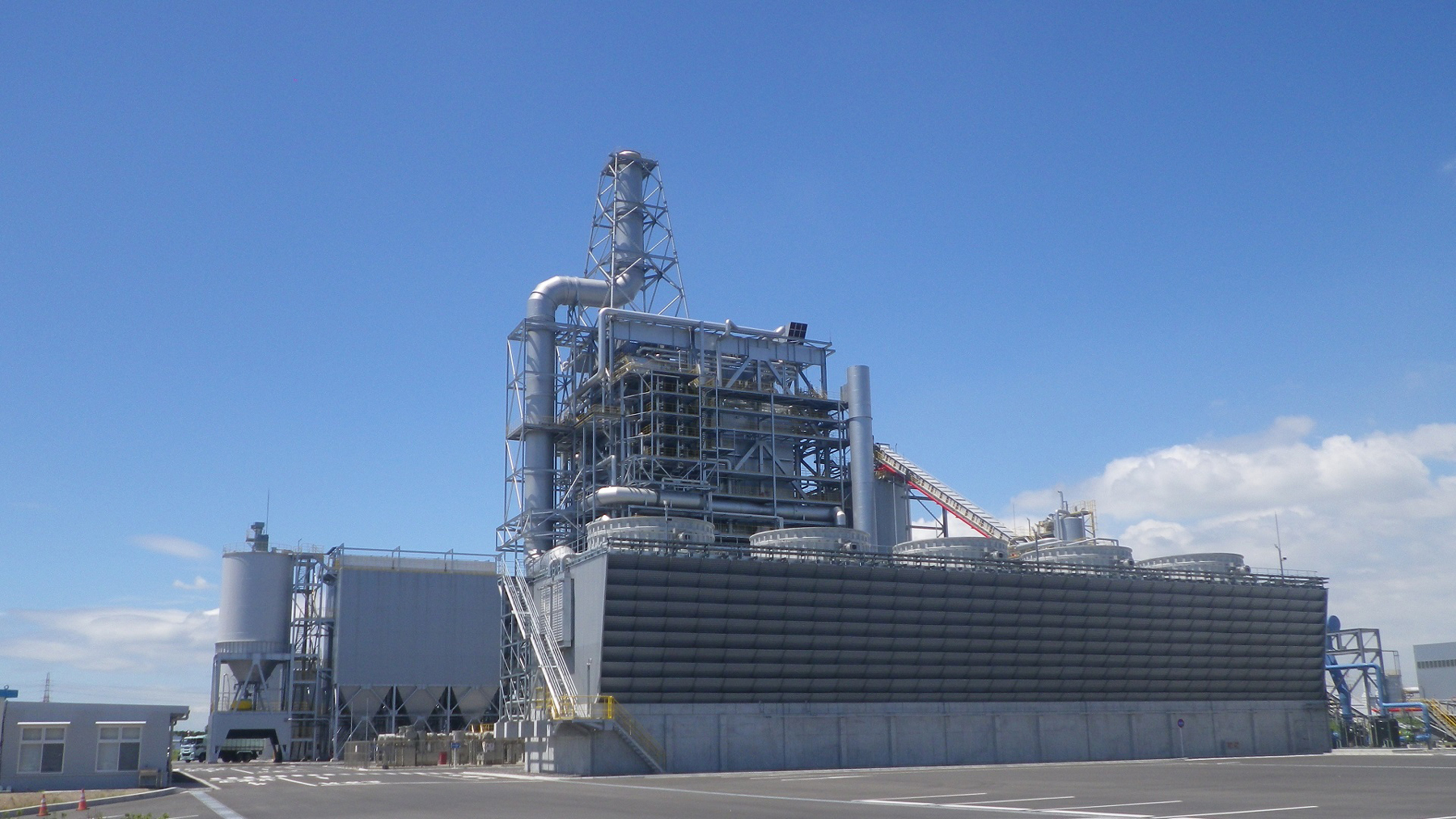
Construction of wind power plants came into full swing in Japan in the early 2000s, before mega-solar projects gathered momentum. Sumitomo Corporation started the commercial operation of its first wind power plant in 2004, when wind power generation had just begun to take off. We then launched several projects, including those in Kashima, Ibaraki Prefecture and Oga, Akita Prefecture, which are well into the operational stage today. In April 2025, a new onshore wind farm—among the largest in Japan—officially commenced commercial operations in the Abukuma region of Fukushima Prefecture.
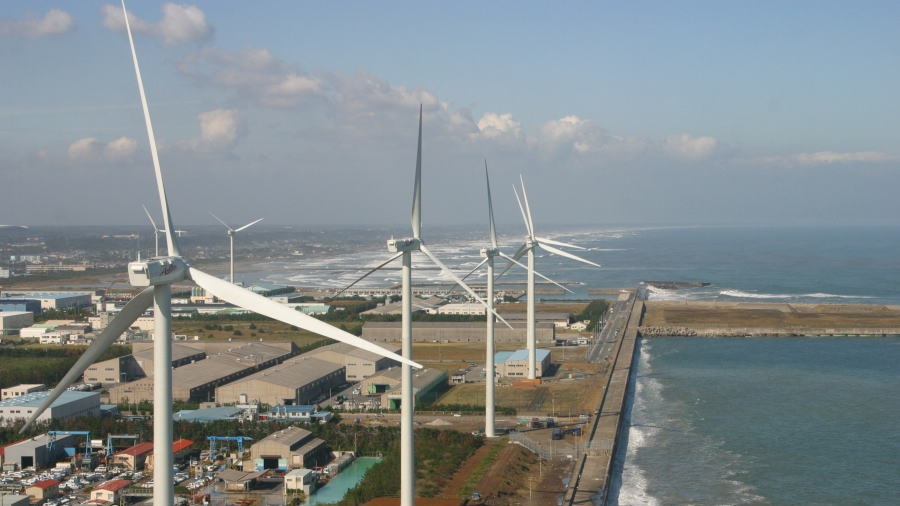
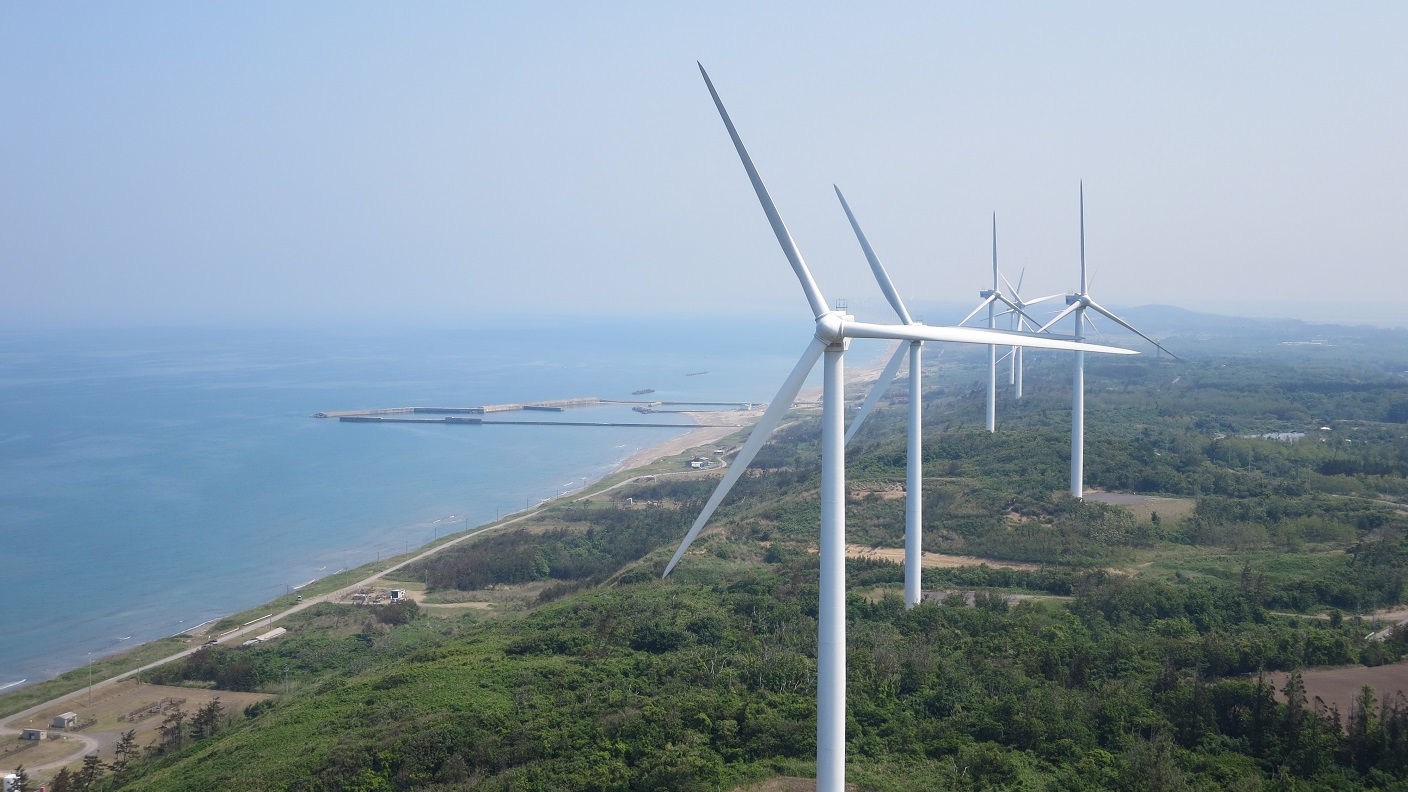


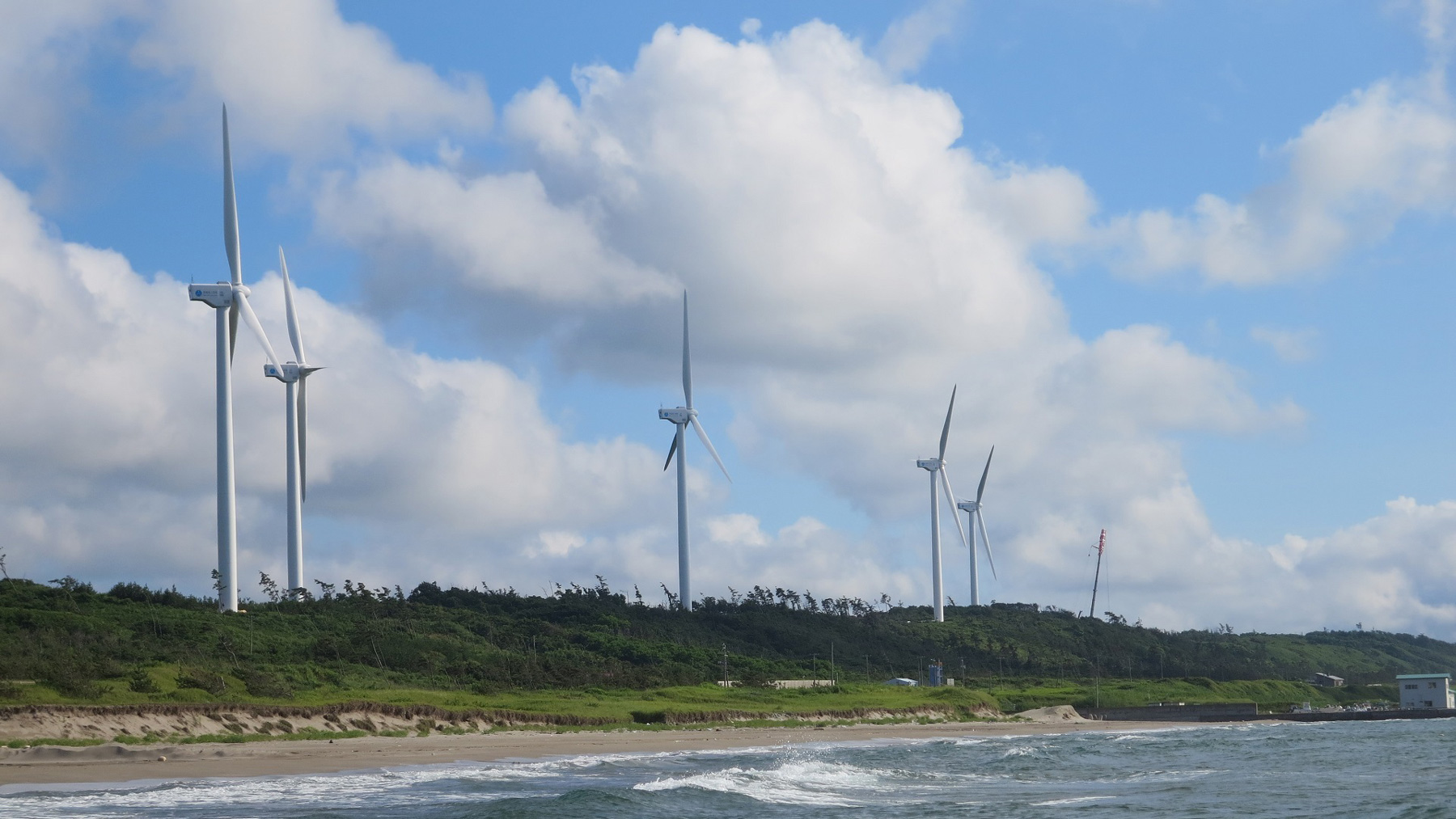
Transforming Fukushima into a leading region for renewable energy through the Abukuma Wind Power Project
In April 2025, under the Fukushima Renewable Energy Promotion Vision and the Fukushima New Energy Society Concept, the Abukuma Wind Power Plants No.1, No.2, No.3, and No.4 (hereinafter collectively referred to as "the Abukuma wind farm"), which had been under construction since April 2022, officially commenced commercial operations under the Feed-In Premium (FIP / *1) system.
The Abukuma wind farm is one of Japan's largest onshore wind farm, with 46 wind turbines, each with a capacity of 3,200 kW, installed on ridgelines in the Abukuma region, spanning the municipalities of Tamura, Okuma, Namie and Katsurao in Fukushima Prefecture. The total generating capacity of the wind farm is approximately 147,000 kW, with an expected annual generation equivalent to the electricity consumption of approximately 120,000 households.
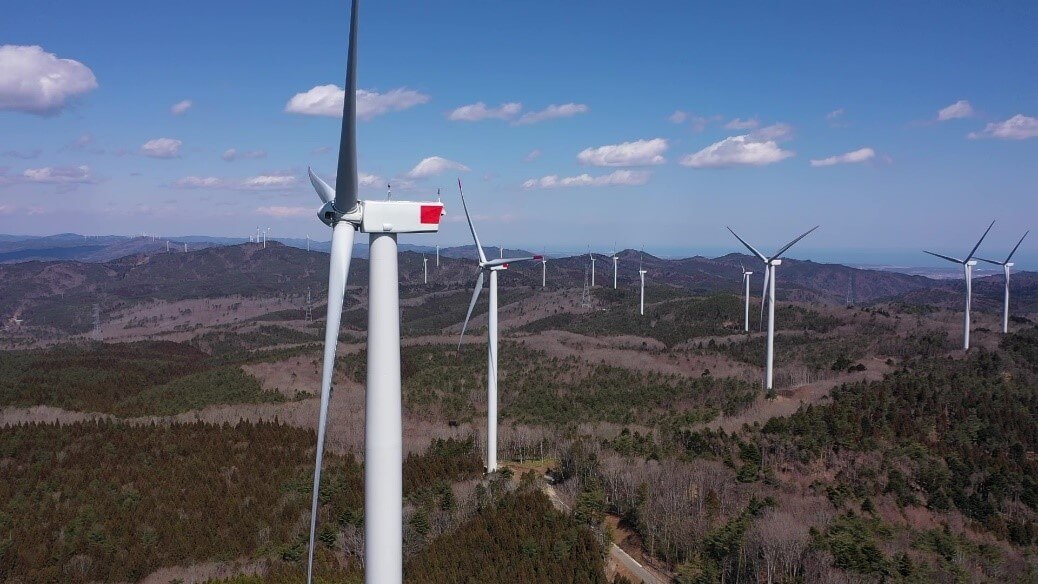

The renewable energy generated at the Abukuma wind farm will be supplied to multiple companies and municipalities with business operations in Fukushima Prefecture through Corporate Power Purchase Agreements (PPA / *2). A portion of the revenue from energy sales will be utilized for funding reconstruction projects in local municipalities where the wind farm is located through the Fukushima Prefecture Renewable Energy Reconstruction Promotion Council.
The Abukuma Wind Power Project will continue to contribute to Fukushima Prefecture’s reconstruction efforts through the stable operation of the wind farm and its returns to the local community. Fukushima Prefecture aims to establish its position as a leading region for renewable energy by generating an amount of renewable energy equivalent to more than 100% of its total energy demand, and this project plays a role in supporting that vision.
*1 FIP = Feed-in-Premium System. A system that provides a premium subsidy for electricity sold by renewable energy generators to encourage investment and promote the expansion of renewable energy. Electricity is sold on the wholesale power market or directly to individual power consumers.
*2 PPA = Power Purchase Agreement: A long-term agreement for purchasing renewable energy from power producers.
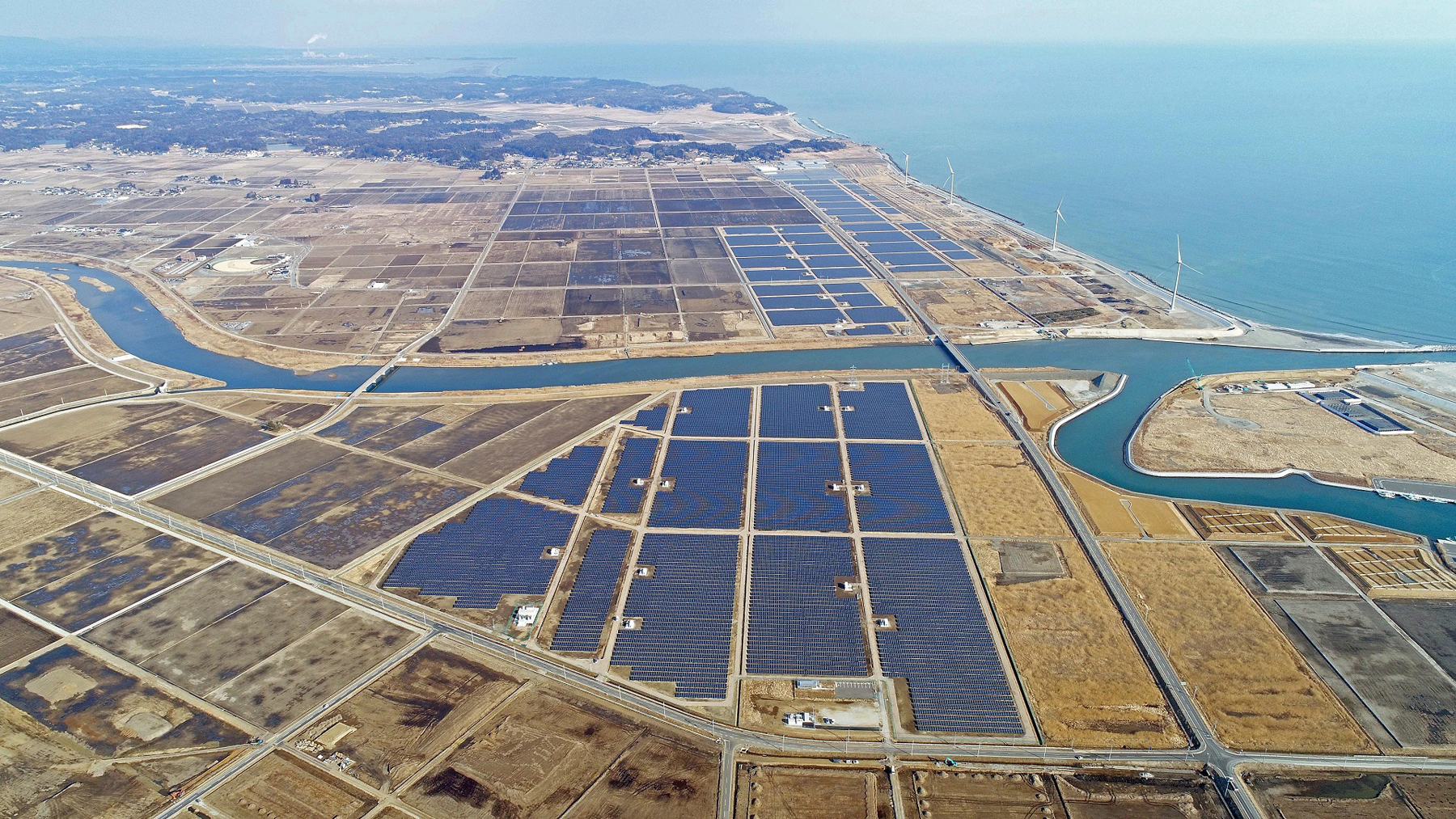
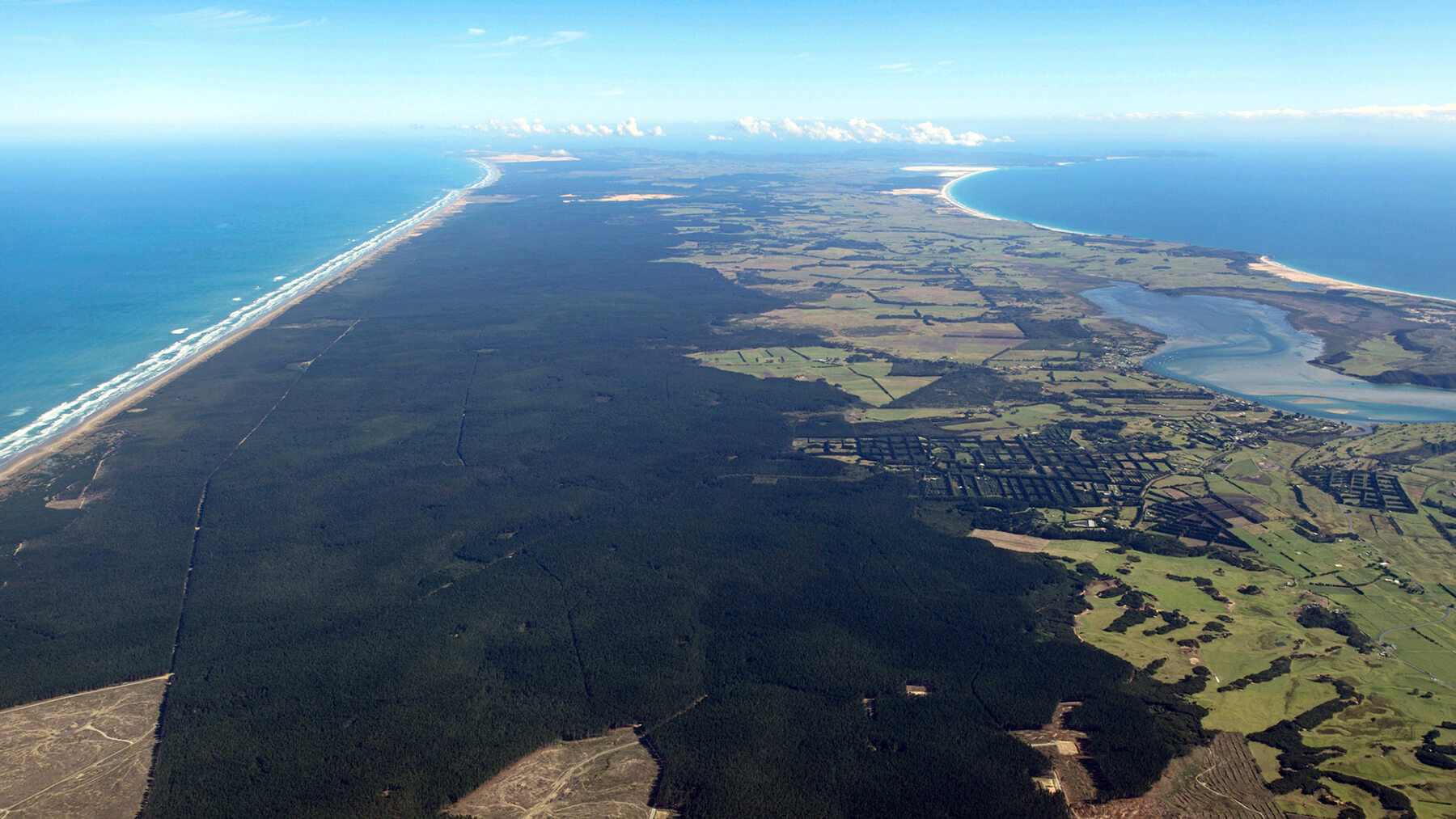
Solar power plants in Minamisoma stand as a symbol of restoration from the earthquake disaster
Our latest initiative in solar power generation is the development of a mega-solar power plant with a generation capacity of 92,000 KW in Minamisoma, Fukushima Prefecture, which suffered devastating damage from the Great East Japan Earthquake. In 2012, one year after the earthquake disaster, we began drawing up a plan to build a solar power plant with cooperation from the local municipality with the aim of making use of coastal land that subsided due to the tsunami. After overcoming numerous challenges, commercial operation commenced in March 2018 for the first phase of construction, and in December 2018 for the second phase of construction.
Fukushima Prefecture aims to expand its renewable energy power generation capacity to meet 100% of the prefecture's demand by around 2040. Installed on a vast plot of 150 ha land, which is 32 times the size of the Tokyo Dome stadium, the two solar power plants will not only contribute to achieving this target, but also stand as a symbol of restoration from the disaster for the regional people.
Sumitomo Corporation has the vision of operating its plants over the long term, even after the Feed-in Tariff period has ended, to continue supplying environmentally friendly and cost-competitive electricity to society. The prerequisite for fulfilling this vision is to build a relationship of trust with the local communities. The only way our facilities can sustain operations over decades to come is to be accepted and loved by the local people.
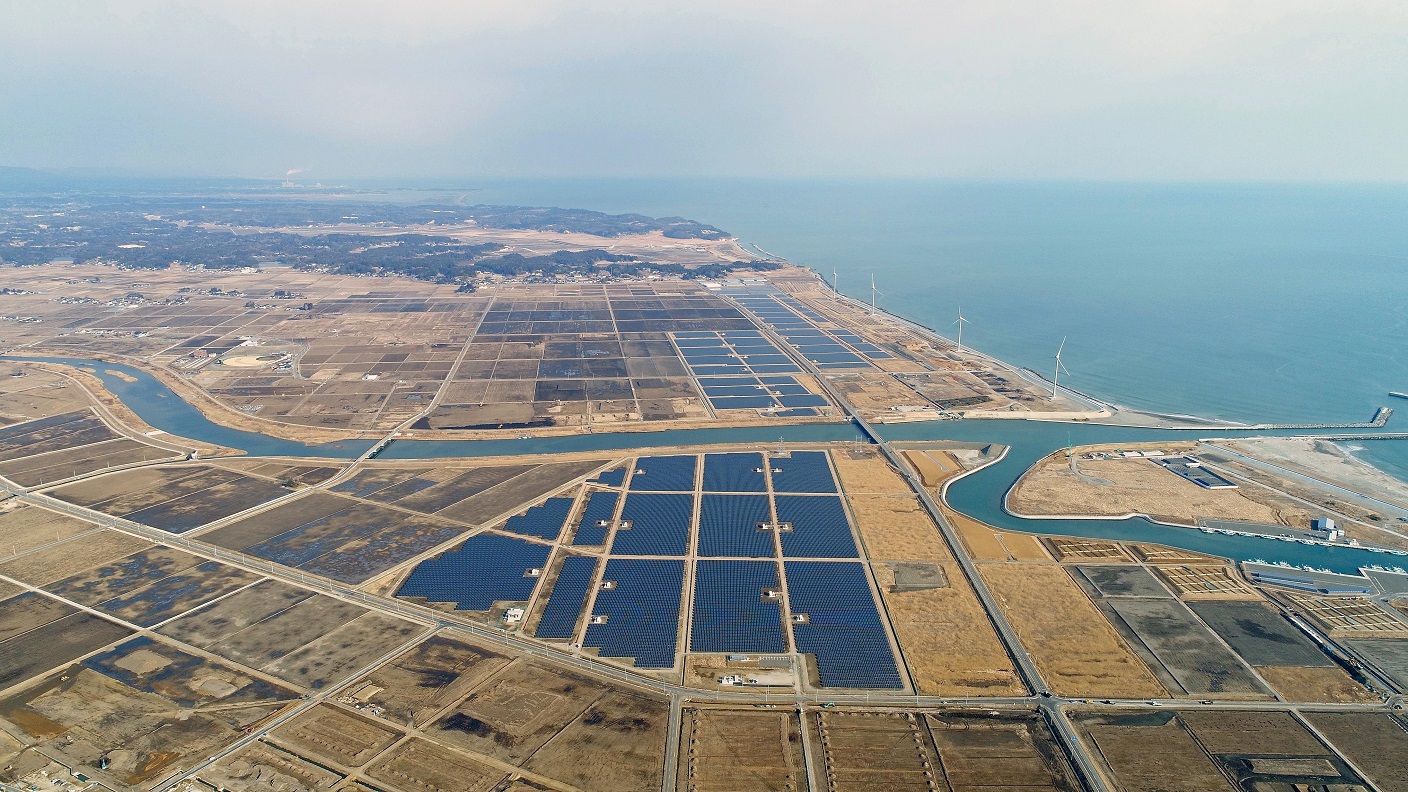
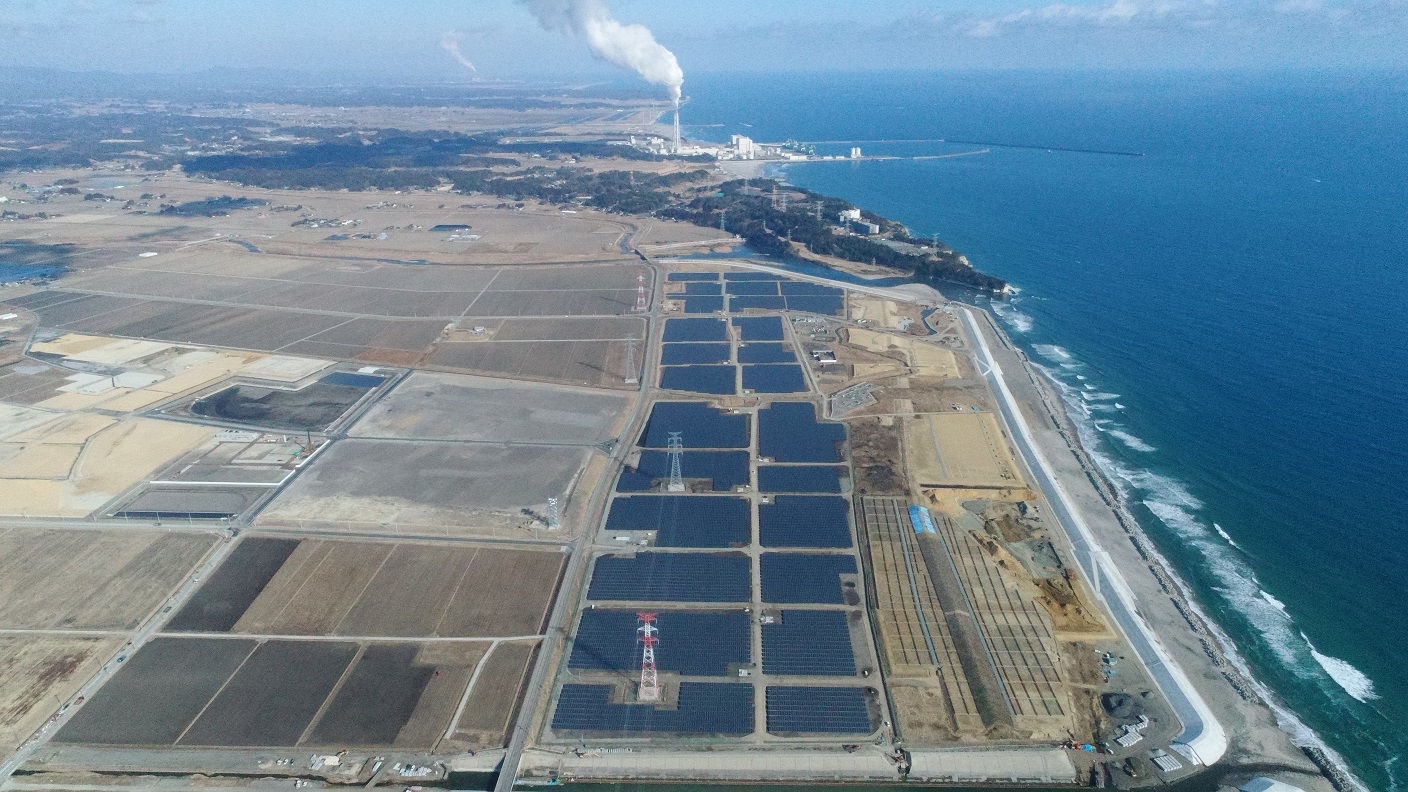


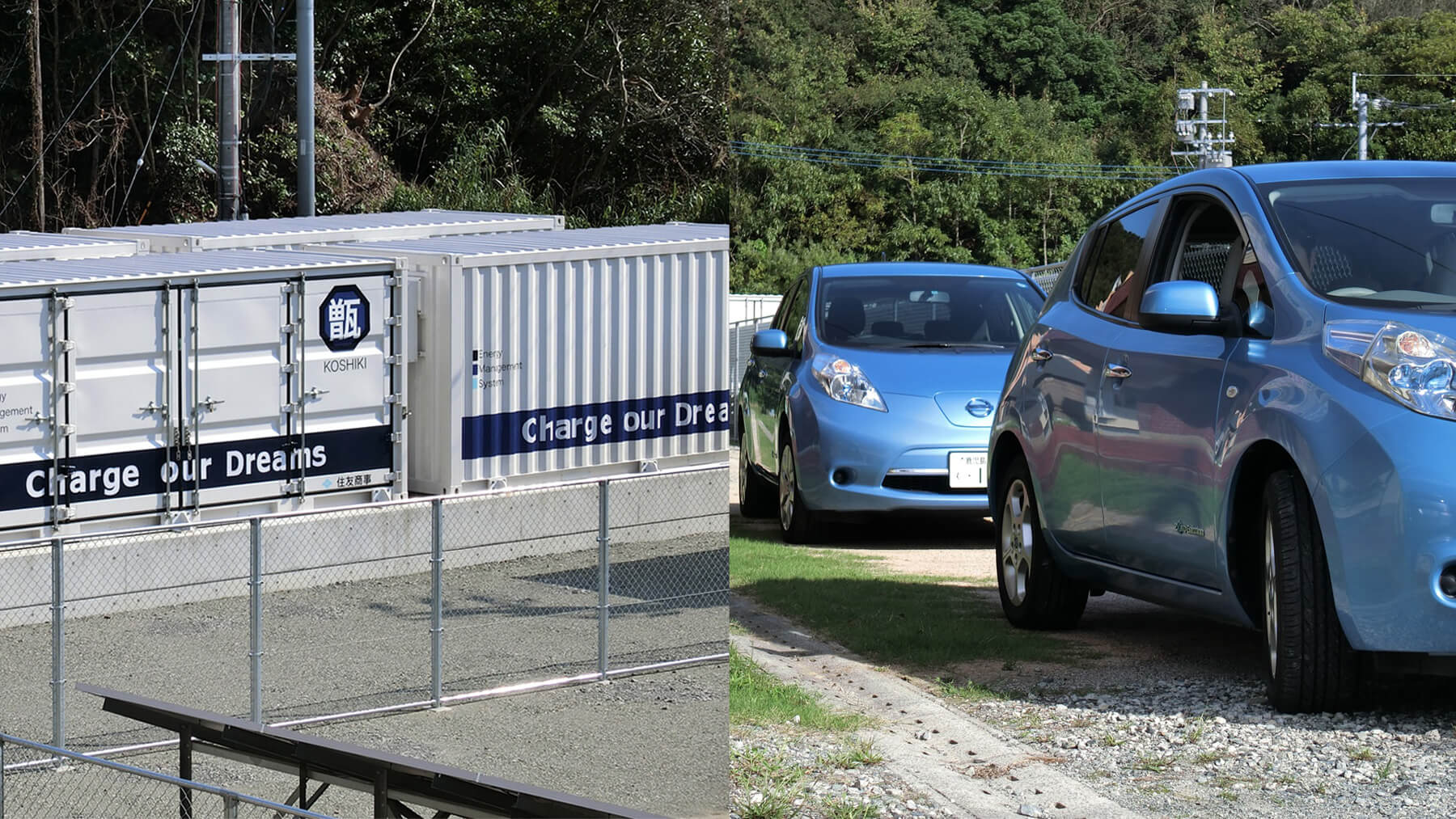
Realizing optimal electricity management through Group-wide collaboration
Solar and wind power generation is susceptible to weather conditions. As a means of compensating for this weakness and ensuring stable electricity supply, Sumitomo Corporation is looking to use the storage batteries in its renewable energy business in pursuit of optimal electricity management. Furthermore, we are seeking to supply the electricity continuously and stably to consumers, in cooperation with Summit Energy Corporation, a subsidiary engaged in electricity retail business, who own and operate large-scale biomass power plants within the Group.

Developing new renewable energy power generation projects
The Japanese government has set the 2040 target for the proportion of renewable energy in the domestic energy consumption mix to up to 40~50%. The Sumitomo Corporaton Group meanwhile, has a medium-term goal of increasing its renewable energy power supply capacity to at least 3 GW in combined total by 2030 and, toward this end, is expanding the development of carbon-free energy projects.
Regarding offshore wind power generation in Japan, which has been attracting attention, we were appointed as the operator for the project off the coast of Enoshima island, Saikai City, Nagasaki Prefecture, in December 2023 in a tender for selecting offshore wind power operators based on the Act on Promoting Utilization of Sea Areas in Development of Power Generation Facilities Using Maritime Renewable Energy Resources implemented by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. We are currently proceeding with various surveys and design work in preparation for the start of commercial operation in August 2029, but we are also implementing various fishery promotion measures and regional development measures, aiming to be a business that is integrated with the local community.
Drawing on our long years of operational experience in solar, wind and biomass power generation, we are confident that we can contribute to the development of Japan's renewable energy power generation industry and the realization of a sustainable society.