- TOP
- Enriching+TOP
- Local 5G into the Future: Smart Factory
2023.10.1
Business
Local 5G into the Future: Smart Factory

In 2020, which was considered the first year of 5G*1, a variety of businesses expressed their plans to enter the 5G and local 5G*2 business. Sumitomo Corporation branched out into the 5G business quickly. Sumitomo Corporation is involved in a wide range of business areas, including CATV and communications, and has been pursuing digital transformation (DX) as one of its business strategies. The company is now working to implement "5G infrastructure X DX," one of which is "local 5G X Smart Factory*3."
In January 2021, Sumitomo Corporation commenced three-month field trials*4 of automated visual inspections and remote quality monitoring at the Osaka Factory of Summit Steel, a subsidiary of Sumitomo Corporation Global Metals and conducting metalworking business. The field trials were conducted to make use of local 5G to find solutions to problems for factories in the future. I participated in a plant tour in March. (For features of 5G and local 5G and the background of the 5G businesses of Sumitomo Corporation, see this November 2019 article.)
What will be the future brought with the next generation of communication, 5G and local 5G
*2 Local 5G: A mechanism in which municipalities and businesses can build and operate their own 5G communication networks in limited areas
*3 Smart factory: A system that improves quality and productivity, and performs automation and visualization by introducing AI and IoT into factories and utilizing digital data
*4 The project was selected by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications as a FY2020 Development Demonstration for Realizing Local 5G to Solve Local Issues.
This content was originally published in July 2021.
-

Mass Media Relations Team, Corporate Communications Department
Haruka Nukaya
Since joining Sumitomo Corporation in 2018, I have been in charge of media relations for the Media & Digital Business Unit, Living Related & Real Estate Business Unit, and Infrastructure Business Unit. Up until recently, I enjoyed posting photos of my parents’ dog and cat on social media and receiving many likes from my fellow dog- and cat-lovers. Now, I have a dog of my own. My dog's favorite snack is Hartz® BABY CHEWDENT (chew with chicken flavor). Hartz® products, which are very popular in the U.S., are marketed in Japan by Sumitomo Corporation and Summit Agro International, which is a member of the Sumitomo Corporation Group. I recommend that dog- and cat-lovers try giving CHEWDENT items to their furry companions.

- Summit Steel Osaka Factory Striving to Support Manufacturing
- Smart Factory Realized via Local 5G
- Rising Expectations for Local 5G
- Field Trials Utilizing the Integrated Corporate Strength of the Sumitomo Corporation Group
- Extending the Project to other Partners
- (Addendum) 5G Business Dept. Building 5G Network Early
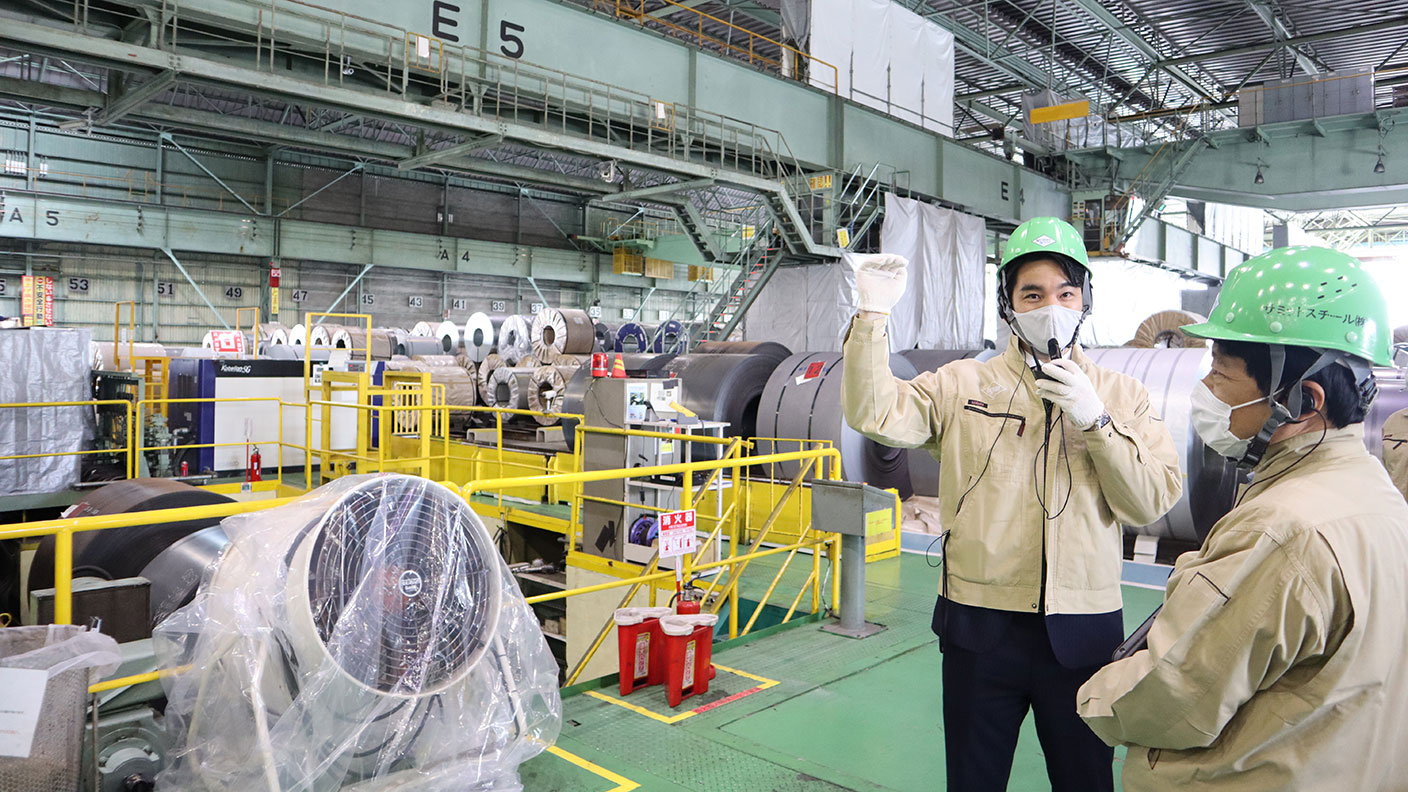
Summit Steel Osaka Factory Striving to Support Manufacturing
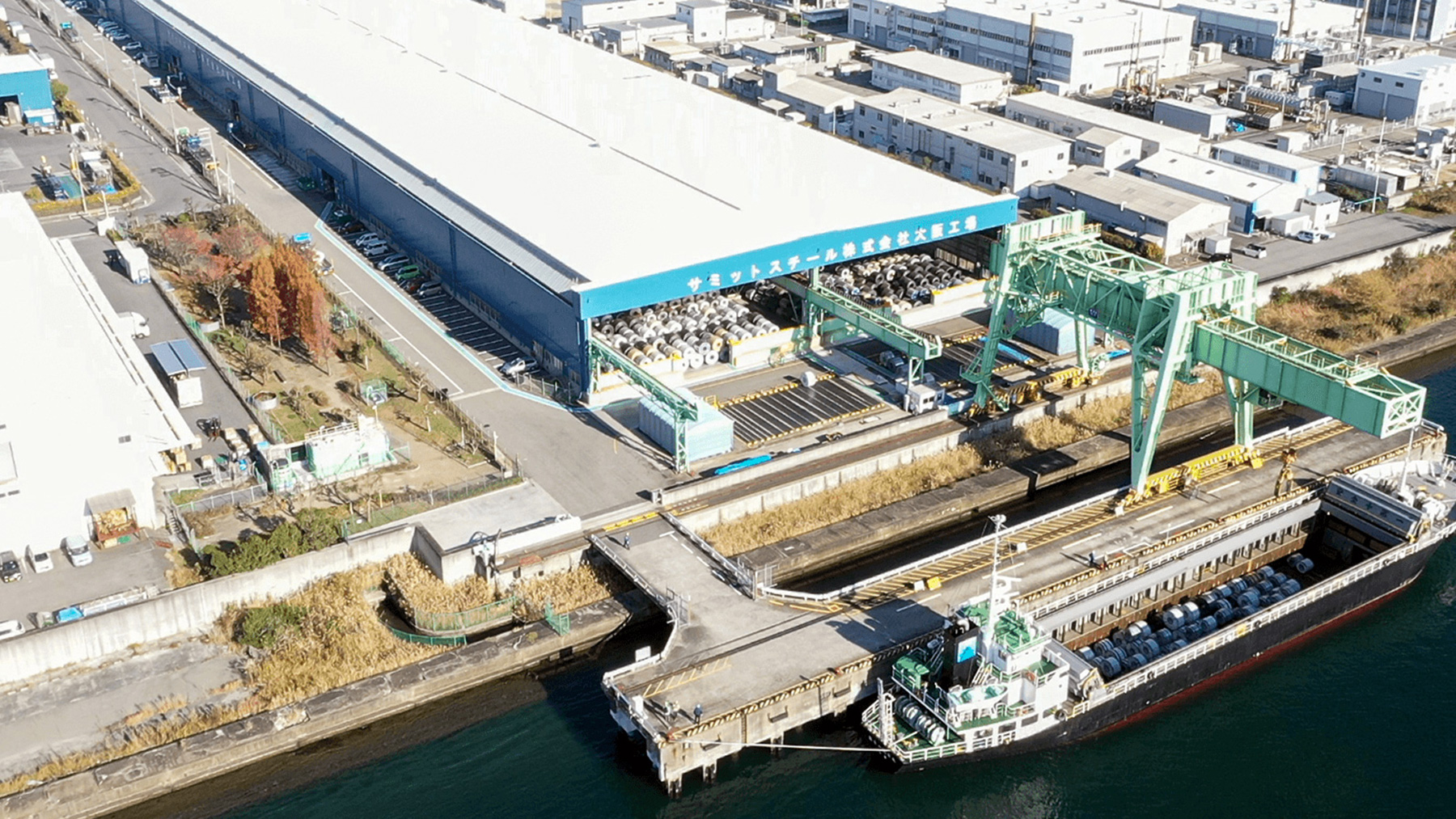
The Summit Steel Osaka Factory is one of the largest sheet steel processing plants in Japan. The factory, located in a gulf region in Konohanaku, Osaka, receives giant coils of sheet steel from steelmakers and cuts and processes them into forms desired by its customers. Processed sheet steel is supplied to electrical home appliance and office automation industries, housing industries, building material manufacturers, and automakers, and is employed in goods commonly used in our daily life. The factory has its own landing facility that can accommodate a 3,000-ton class ship, as well as a large warehouse; that is, the factory is a site for one-stop service, from landing through unloading, storing, processing, and forwarding.
Having never visited a sheet steel processing plant before, I was overwhelmed at the sight of more than hundred gigantic coils being stored there. It is amazing that those gigantic coils require very delicate work. Even a slight impact on the sheet steel can result in a flaw or dent. Such flawed sheets are scrapped and shredded into pieces; therefore, flaw detection is very important in the processing factory.


Smart Factory Realized via Local 5G
At a slitting line, where coils are unwound, slit, and cut into narrower strips, field trials were carried out to demonstrate automated visual inspection of surface flaws and remote quality monitoring.
Traditional steps are as follows: The worker visually inspects the in-process coil. If there is a flaw, the worker checks its depth, size, color, and other conditions. The worker takes photos of the flaw and shares them with the head office sales department. Considering the customer’s requirements, the head office sales department decides from the photo whether the product can be shipped or not. If the decision cannot be made on the basis of the photo alone, the sales department staff comes to the factory to observe the flaw.


Local 5G completely changed the traditional process. The 8K line-scan camera used in the automated visual inspection has a high-speed continuous scanning capability and a high inspection accuracy. The camera sends high-definition images of the coil to an AI server via wireless local 5G, and AI determines whether a flaw is present. The location of the flaw in the coil is detected on the basis of transmitted data. High-definition video sent from a 4K camera operated by the on-site worker enables the sales department to monitor quality at the head office. Very small flaws can be identified from a remote location.
Visual checks of very small flaws on coils, which can be a minimum of about 0.3 millimeters wide, had formerly been entrusted to skilled workers. They sometimes devoted themselves single-mindedly to observing coils in a squatting position. Akiharu Kirimura, executive officer, assistant general manager of the Production Division and manager of the Production Control Department at Summit Steel, received positive reactions from on-site workers that their physical and mental burden could be lightened. The staff from the head office required one hour or more to go to the factory and back if an on-site check was needed. Current COVID-19 infection makes it difficult to access the factory. There is an increasing need for remote quality monitoring. On-site problems are expected to be solved by improving safety and productivity, such as reducing the total person-hours needed to complete work, lightening physical and mental burden, and reducing dangerous work required in the vicinity of the running line.
The project requires transmission of high-definition images and video, such as 8K images and 4K video. This requirement can be met by 5G, which is able to transmit a large quantity of data. Cables laid on the floor could be problematic in terms of safety and extensibility, and should be avoided. Local 5G that secures a stable network in a limited region is best suited to tasks that need to ensure a high degree of accuracy, such as automated visual inspections and remote quality monitoring.
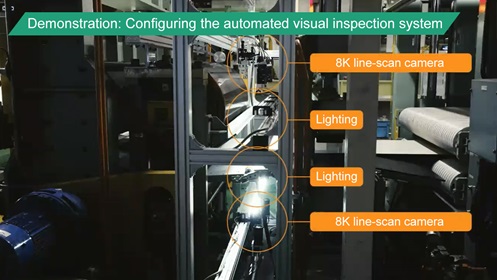
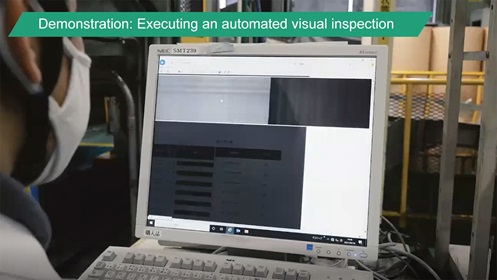

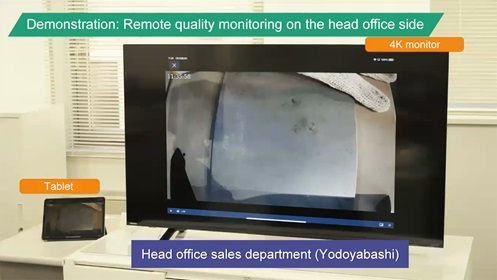
Rising Expectations for Local 5G
The demonstration was considered from two aspects: solving problems in the factory and evaluating performance such as radio transmission by local 5G and speed. The results are given below.
In automated visual inspection, 8K images were sent successfully in the local 5G environment. Some challenges with regard to accuracy remain with AI inspection. By improving accuracy, the total person-hours needed to complete a visual check can be reduced. To keep pace with visual inspection, coils are currently processed at the relatively low speed of 20 meters per minute. If AI flaw detection replaces the current visual inspection, both flaw detection and coil processing are expected to be conducted at a speed exceeding 100 meters per minute. Detection time can be reduced and more coils can be processed.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications allocates two frequency bands, Sub6 (4.5-gigahertz band) and millimeter wave (28-gigahertz band), to local 5G. The Sub6 band institutionalized in December 2020 is close to the 4G band of carriers and is less likely to be affected by blocks. Thus, the indoor wireless area can be designed easily. Millimeter waves institutionalized in December 2019 have a strong tendency toward straightness and are likely to be affected by blocks. The broad frequency range of millimeter waves enables a larger quantity of data to be transmitted at a higher speed compared to the Sub6 band. Either frequency band is selected to meet the needs of the site.
Sumitomo Corporation conducted a field trial in the millimeter band in June 2019*5. The demonstration described here was conducted in the Sub6 band because the site comprises a factory with many blocks. The demonstration proved that the antenna of a single local 5G base station can cover a wide range in the factory, which is 64 meters deep, 344 meters wide, and 14 meters high. Although a variety of metal products and pieces of equipment in the factory block radio waves, wide coverage can nonetheless be realized. High diffraction and reflection of the Sub6 band was confirmed.
The field trials raised expectations about local 5G in Smart Factory, which is the digital transformation (DX) of factories. Yasuhiro Akita, President of Summit Steel, said, "The company can upgrade by reducing the workload at the site and improving efficiency. Safety comes first in factories. Keeping humans away from machines is the best way to achieve this. With the demonstrated system, safety can be improved further." By adopting the same system at other sites in the future, the head office can connect with other factories, and all the factories can connect with each other. The system will also enable many other applications, such as sharing information with customers, suppliers, and equipment maintenance companies in real time.

*5 First outdoor and indoor field trials using the millimeter band in Japan. The influence of variations in communication distance, blocks such as buildings, and variation in elements on wireless communication was verified outdoors as well as indoors.
Field Trials Utilizing the Integrated Corporate Strength of the Sumitomo Corporation Group
In the framework to conduct the field trials, the Sumitomo Corporation Group played a predominant role. Sumitomo Corporation Global Metals was in charge of the problem-solving demonstration and selected the Summit Steel Osaka Factory as the site of the demonstration. Sumitomo Corporation Global Metals is a trading company specializing in steel and has steel processing factories in many locations around the world. Making the most of its rich experience both in the trading business and in managing factories, the company is making positive efforts to promote its own digital transformation.
Takayoshi Suzuki, Digital Innovation Team, Sumitomo Corporation Global Metals, explained the reason that the company participated in the field trials. "We have acquired factory operation data for visualization over a long period of time, so we have been interested in local 5G, which allows the use of high-volume data. Led by the 5G Business Dept. of Sumitomo Corporation, in July 2019, we had an interview. As a part of the project on sophistication by digital technologies at the Summit Steel Osaka Factory which we were implementing at that time, we participated in the demonstration project."

A team of about 20 colleagues inside and outside the company has worked in the project for about one and a half years. Suzuki said, "We will continue to listen to the voices of on-site workers, calculating the cost, person-hours, and period, and determining effectiveness. We are striving toward further improvement and sophistication through the use of digital technologies."
Sumitomo Shoji Machinex has led the team and configured the environment for a performance demonstration. Local 5G systems used in the project are provided by GRAPE ONE, which was established in 2019 by Internet Initiative Japan, several cable operators, and Sumitomo Corporation. GRAPE ONE has the mission-critical control system needed to expand local 5G and provides general services pertaining to local 5G, such as sales, operation, and maintenance of base stations and terminals.
Extending the Project to other Partners
Makoto Ishiguro, 5G Business Dept., Sumitomo Corporation, is determined. "With the Integrated Corporate Strength that the Sumitomo Corporation Group has built in handling a variety of businesses, we can obtain further findings. We will accumulate experiences, striving toward the implementation of ‘digital transformation X local-5G infrastructure,’ and will accelerate digital transformation via local 5G in different industries."
With local 5G, special networks are built for individual companies. Compared to 5G networks provided by carriers, the special network can be designed to satisfy the needs of the company and appears to be resistant to communication failures caused by congestion. In regions where carriers have not yet provided 5G, licensed companies can build their own local 5G networks. Factories, construction sites, farms, and river disaster prevention bases are expected to have local 5G networks.
Ishiguro assumes that there are many people worrying about how to solve problems at the site and how to use 5G. Based on findings accumulated by the Sumitomo Corporation Group, the Group should make concrete suggestions such as feasible methods at construction sites.
After the plant tour, I recognized that the "Smart Factory system X Local 5G" is based on the wisdom and efforts accumulated by quite a large number of people. The staff members have worked hard to conduct the field trials at the functioning factory during the hardship brought about by the COVID-19 epidemic. They are ready to offer their partners the know-how they have acquired through their work if it is needed to make improvements. Please do not hesitate to contact Sumitomo Corporation if you are interested in local 5G and its potential in many fields.

(Addendum) 5G Business Dept. Building 5G Network Early
Sumitomo Corporation has been involved in CATV businesses since 1984. Based on close association with cable operators and local regions and findings acquired from telephone, internet, and other communication services, Sumitomo Corporation was able to start its 5G project early. The company has also put efforts into sharing 5G base stations.
The 5G network uses a high frequency band and has small coverage of radio transmissions. Thus, the network requires five to ten times the number of base stations needed for 4G and also requires increased capital spending. Since it is difficult to acquire sites for new base stations in densely populated midtown areas, demand for shared base stations will increase.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications set a goal of promoting shared base stations, for example, in its Master Plan 3.0 on the Regional Development of ICT Infrastructure. Expectations for shared base stations are running high in terms of sustainable development goals (SDGs). By sharing equipment and materials, power can be saved and the business model is considered to be "green."
Tokyu Corporation and Sumitomo Corporation established Sharing Design in February 2021 to enable early preparation of 5G. Sharing Design provides base-station sharing services and builds infrastructure by placing base stations, which used to be done separately by different companies. By sharing equipment, economic burden on carriers can be relieved, and electric bills as well as other operation expenses can be lowered.
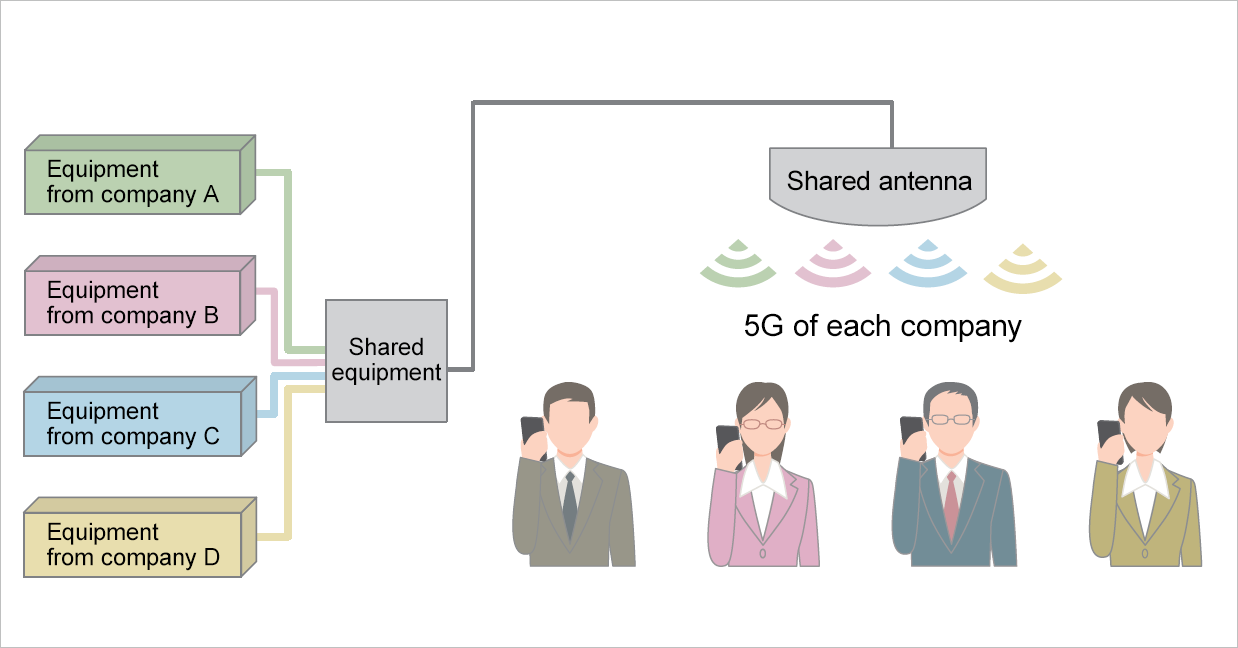
Sharing Design is planning to start services for mobile operators in October 2021 and place base stations at about 100 sites, including stations on Tokyu Lines and Tokyu commercial facilities, by the end of fiscal 2021. Sharing Design is aiming at expanding its business country-wide through cooperation with municipalities, railway operators, and commercial facility operators.
The company is conducting several demonstration projects for sharing base stations.
Sumitomo Corporation has acquired know-how through overseas mobile businesses. Sumitomo Corporation has extensive experience in businesses such as management of the communication-equipment supply chain and holding communication infrastructure in cable businesses. Based on the acquired findings and know-how and the Integrated Corporate Strength of the Group, Sumitomo Corporation strives to create next-generation businesses utilizing 5G and local 5G.






















